快速水解生物质New US Patent Issued for ‘Fast Hydrolysis’ Process for Biomass
Fast Hydrolysis Process of Biomass快速水解生物质
According to USPTO Public PAIR, a U.S. patent #: US8268126 has been issued to Zhen Fang (Kunming, CN) and Chun Fang (WA, US) for technology that provides a simple and low-cost method to fast dissolve and hydrolyze lignocellulosic biomass with great potential for a novel biorefinery.
The patent entitled “Method, equipment and applications for fast complete dissolution and hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass” was issued on September 18, 2012 for work done by Professor Zhen Fang, Leader and Founder of Biomass Group at Chinese Academy of Sciences. Professor Fang stated, “We are very excited to have been granted this new U.S. patent containing such claims that provide protection for ‘fast hydrolysis’ process.
In previous work, Sasaki et al. [1] found that microcrystalline cellulose could be completely dissolved in water at temperature above 320 oC and became a ‘cellulose solution’, which made it possible to build up a continuous flow reactor for the rapid hydrolysis of cellulose. Continuous reaction of microcrystalline cellulose (20 wt%) in water at supercritical conditions (> 374 oC and 22.1 MPa) gave water-soluble products (with 100% conversion) containing 80% hydrolysates (glucose and oligomers) for short reaction time (ca. 0.05 s) [1]. However, the separating of pure cellulose from actual biomass (e.g., wood) is complicated and costly. It is difficult for the solubilization and hydrolysis of pure cellulose to be commercialized. Thus, it is necessary to find a method for complete dissolution of actual lignocellulosic biomass and for further refining to value-added products.
Fang et al. [2] found that by adding 0.8 wt% Na2CO3, actual wood without pretreatment can be completely dissolved upon fast-heating (7~16°C/s) to form a ‘wood solution’ at 329-367 oC at short reaction times (0.7-2 s). The ‘wood solution’ can be rapidly (ca. 15 s) hydrolyzed to sugars/sugar oligomers under homogeneous conditions.
Based on the above work, a ‘fast hydrolysis’ process was invented for actual lignocellulosic biomass:
(a) Placing lignocellulosic biomass (wood or grass particles) in 1.9~10 wt% alkaline solution, and keeping biomass/liquid ratio at (0.003~1.05)/1, as sample 1;
(b) Heating pure water to a temperature between 329~367 °C, as sample 2;
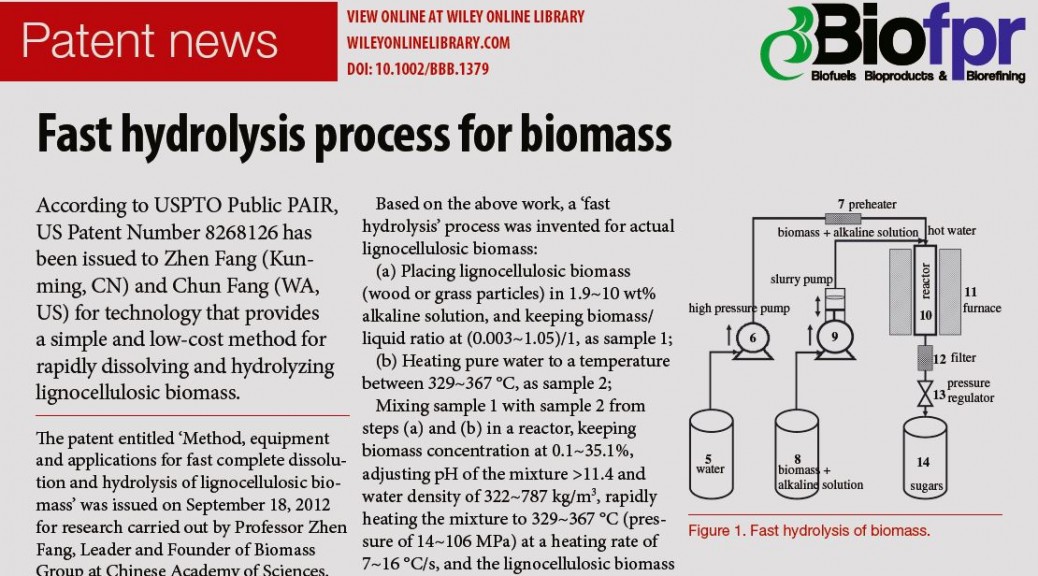
Mixing sample 1 with sample 2 from steps (a) and (b) in a reactor, keeping biomass concentration at 0.1~35.1%, adjusting pH of the mixture >11.4 and water density of 322~787 kg/m3, rapidly heating the mixture to 329~367°C (pressure of 14~106 MPa) at a heating rate of 7~16°C/s, and the lignocellulosic biomass will completely dissolve in 0.7~2 s to form ‘biomass solution’ that is further rapidly hydrolyzed in a homogeneous phase to sugars and sugar oligomers. In Fig. 1, an equipment was proposed for the continuous ‘fast hydrolysis’ process.
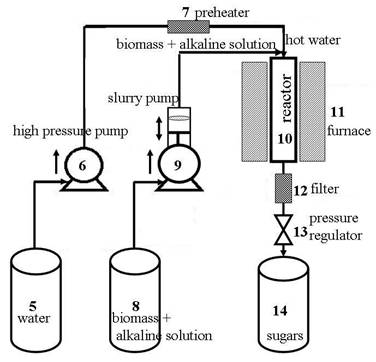
Fig. 1. Fast Hydrolysis of Biomass图1.快速水解生物质
The patent is the latest development in a 23-year effort by Professor Zhen Fang in the study of biomass hydrolysis process, aimed at a simple, fast and low-cost method for a novel biorefinery. ‘Fast hydrolysis’ process will be the technological key to economic utilization of abundant lignocellulosic biomass as viable feedstocks for the production of industrial sugar, ethanol and chemicals. His pioneering work opens the door, for the first time, to the possibility of developing industrial-scale technology at competitive cost for producing biofuels and value-added products from lignocellulosic biomass based on the ‘fast hydrolysis’ process in a flow reactor.
This patent is the ninth patent issued to Professor Zhen Fang adding to its portfolio of 3 pending international and 13 pending Chinese patent applications which cover various features of biorefinery technologies.
The newly issued patent is accessible on the USPTO’s website at http://portal.uspto.gov/external/portal/pair.
Fast Hydrolysis Process of Biomass快速水解生物质
根据美国专利商标局公共PAIR,方真(中国昆明)和方纯(美国华盛顿州)已获得美国专利号:US8268126,该技术提供了一种简单、低成本的方法来快速溶解和水解木质纤维素生物质,具有巨大的新型生物精炼潜力。
“木质纤维素生物质快速完全溶解和水解的方法、设备和应用”专利于2012年9月18日授予中国科学院生物质组组长兼创始人方真教授。 方真教授表示:“我们很高兴获得这项新的美国专利,其中包含为‘快速水解’过程提供保护的权利要求。”
在之前的工作中,Sasaki等人[1]发现微晶纤维素在320 ℃以上的温度下可以完全溶解在水中,成为“纤维素溶液”,这使得建立一个用于纤维素快速水解的连续流反应器成为可能。微晶纤维素(20 wt%)在超临界条件下(>374 ℃和22.1 MPa)在水中连续反应,在短反应时间(约0.05秒)内得到含有80%水解产物(葡萄糖和低聚物)的水溶性产物(转化率为100%)[1]。然而,从实际生物质(如木材)中分离纯纤维素是复杂且昂贵的。纯纤维素的增溶和水解很难商业化。因此,有必要找到一种完全溶解实际木质纤维素生物质并进一步精炼成增值产品的方法。
方真等人[2]发现,通过添加0.8 wt%的Na2CO3,未经预处理的实际木材在快速加热(7~16 °C/s)时可以完全溶解,在329-367 °C下以短反应时间(0.7-2 s)形成“木材溶液”。“木溶液”可以在均匀条件下快速(约15秒)水解成糖/糖低聚物。
基于上述工作,为实际的木质纤维素生物质发明了一种“快速水解”工艺:
(a)将木质纤维素生物质(木材或草颗粒)置于1.9~10 wt%的碱性溶液中,并保持生物质/液体比为(0.003~1.05)/1,作为样品1;
(b)将纯水加热至329~367 °C之间的温度,作为样品2;
将样品1与步骤(a)和(b)中的样品2在反应器中混合,保持生物质浓度在0.1~35.1%,调节混合物的pH值>11.4,水密度为322~787 kg/m3,以7~16 °C/s的加热速率将混合物快速加热至329~367°C(压力为14~106 MPa),木质纤维素生物质将在0.7~2秒内完全溶解,形成“生物质溶液”,在均匀相中进一步快速水解为糖和糖低聚物。在图1中,提出了一种用于连续“快速水解”过程的设备。
该专利是方真教授23年来在生物质水解过程研究方面的最新进展,旨在为新型生物精炼厂提供一种简单、快速、低成本的方法。“快速水解”工艺将是经济利用丰富的木质纤维素生物质作为生产工业糖、乙醇和化学品的可行原料的技术关键。他的开创性工作首次为以具有竞争力的成本开发工业规模技术的可能性打开了大门,该技术基于流动反应器中的“快速水解”过程,从木质纤维素生物质中生产生物燃料和增值产品。
该专利是方真教授获得的第九项专利,增加了其3项未决国际专利和13项未决中国专利申请,涵盖了生物炼制技术的各种特征。
新颁发的专利可在美国专利商标局的网站上访问,网址为http://portal.uspto.gov/external/portal/pair
References参考文献:
[1] Sasaki M, Fang Z, Fukushima Y, Adschiri T, Arai K. Dissolution and hydrolysis of cellulose in subcritical and supercritical water. Ind Eng Chem Res 2000; 39:2883-90.
[2] Fang Z, Fang C. Complete dissolution and hydrolysis of wood in hot water. AIChE J 2008; 54:2751-8.