催化热解制备4-乙烯基苯酚:Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration
星期二, 30 4 月, 2024Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration
Recently, Master student Miss Wen-juan Guo supervised by Dr. Wei Chen and Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article entitled “Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration” in Industrial Crops and Products.
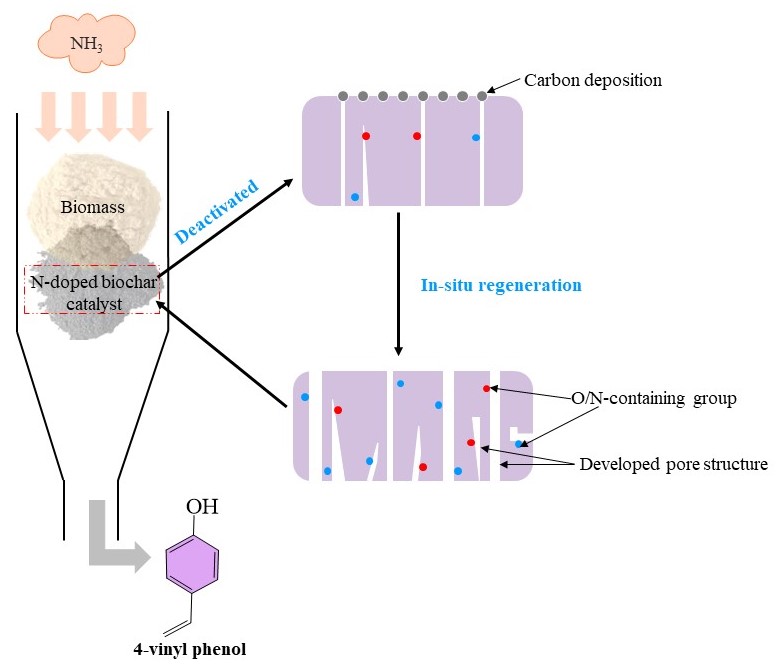
A new catalytic pyrolysis system of biomass was proposed. Nitrogen-doped biochar catalyst was used to pyrolyze bamboo to produce valuable 4-vinyl phenol (2500 yuan/kg) under NH3 atmosphere, and in-situ regeneration of the catalyst was realized. NH3 and nitrogen-doped biochar catalyst could significantly increase bio-oil yield (up to 68 wt.%) and phenols content (80%). The selectivity and absolute yield of 4-vinyl phenol were up to 28% and 5.85 wt.%, respectively. N/O-containing groups in the catalyst and free radicals from NH3 promoted the break of ester bonds and β-O-4 bonds, and converted phenols intermediates to 4-vinyl phenol. Meanwhile, NH3 also acted as activator and nitrogen dopant, which realized the in-situ regeneration of the catalyst. The regeneration rate of nitrogen content and SBET of the catalyst was up to 84.5%-150% and 72.9%-85.4%, respectively. In addition, the nitrogen-doped biochar catalyst also showed good stability and reusability, and the yield of 4-vinyl phenol was still as high as 5.85-6.05 wt.% after repeated use of BC10 catalyst for 3 times. This was also the first time to explore the formation path of 4-vinyl phenol and the in-situ regeneration mechanism of the catalyst, based on the synergistic effect of NH3 and the nitrogen-doped biochar catalyst. It proposed a new direction for the high value utilization of biomass resources.
Related results were accepted in Industrial Crops and Products:
W Guo, Y Wang, W Chen*, GX Xu, G Zhu, GXie, LXu, Zhen Fang, Q Zhang, H Yang. Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration. Industrial Crops and Products (IF = 5.9) (2024) 214, 118520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118520
Selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration原位再生掺氮生物炭催化剂催化热解生产4-乙烯基苯酚
NH3气氛下基于掺氮生物炭催化剂原位再生的生物质催化热解选择性生产4-乙烯基苯酚
最近,硕士生郭文娟在陈伟副教授和方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Industrial Crops and Products (Q1, IF = 5.9) 发表了一篇题为“Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration”的研究性论文。
该研究提出了一种新的生物质催化热解体系,在NH3气氛下采用掺氮生物炭催化剂对竹子进行热解,制备得到了高价值的4-乙烯基苯酚(2500元/kg),与此同时实现了催化剂的原位再生。NH3和掺氮生物炭催化剂可显著提高生物油收率(68 wt.%)和酚类化合物含量(80%)。4-乙烯基苯酚的选择性和绝对含量分别高达28%和5.85 wt.%。催化剂中的含N/O官能团和来自NH3的NH*和NH2*自由基促进了酯键和β-O-4键的断裂,将酚类中间体转化为4-乙烯基苯酚。同时,NH3还作为活化剂和氮掺杂剂,实现了掺氮生物炭催化剂的原位再生,催化剂氮含量和SBET的再生率分别为84.5%-150%和72.9%-85.4%。此外,催化剂也表现出良好的稳定性和可重复使用性,在BC10催化剂重复使用3次后,4-乙烯基苯酚的产率仍高达5.85-6.05wt.%。这项研究也是首次基于NH3与掺氮生物炭催化剂的协同作用探究4-乙烯基苯酚的形成路径和催化剂的原位再生机理,为生物质资源的高值化利用指明了新的方向。
结果发表在Industrial Crops and Products:
W Guo, Y Wang, W Chen*, GX Xu, G Zhu, GXie, LXu, Zhen Fang, Q Zhang, H Yang. Insight into the synergistic influence of nitrogen-doped biochar and NH3 on selective production of 4-vinyl phenol from biomass catalytic pyrolysis by coupling catalyst in-situ regeneration. Industrial Crops and Products (IF = 5.9) (2024) 214, 118520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118520