Direct production of biodiesel from waste oils with a strong solid base from alkalized industrial clay ash
Direct production of biodiesel from waste oils with a strong solid base from alkalized industrial clay ash
Recently, PhD student Miss Wen-jie Cong supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article in Applied Energy about biodiesel production from high acid (AV) waste oils with a solid base derived from spent bleaching clay (SBC).
Biodiesel was directly one-step produced from waste oils without pretreatment catalyzed by a solid base alkalized from SBC ash. Optimized conditions were obtained with 99.1% biodiesel yield from soybean oil with an orthogonal design. The base catalyst was stable within 8 cycles (> 95% biodiesel yield) and resistant to saponification (AV = 9.7 mg KOH/g, 96.5% biodiesel yield). The base was characterized with XRD, EDX-mapping, FT-IR, XRF and TPD, and it had similar strong basicity to Na2SiO3 (0.21 vs. 0.22 mmol/g for Na2SiO3) with active sites of Na2O and CH3ONa evolved from Na2SiO3 and NaAlSiO4 by reactions of NaOH with oxides (e.g., SiO2, Al2O3) in SBC ash. Furthermore, the base was magnetized with magnetism of 6.86 emu/g by carbonizing residual oil in SBC as carbon support and reductant (of Fe2O3 to magnetic Fe3O4 particles). It catalyzed soybean oil to produce biodiesel with 99.2% yield and blended oil (AV = 5.9) to biodiesel with 91.9% yield without any saponification. The catalyst was magnetically separated and reused for 3 cycles with 87% yield. The non-magnetic base could also efficiently catalyze actual SBC oil for the production of biodiesel with 95% yield at AV of 10. This work realized the full use of inorganics in SBC, and its oil for direct biodiesel production at a low temperature (i.e., 65 vs. 120 oC with sulfuric acid process) without wastes produced and results can easily find practical applications for waste oils.
Related results were accepted in Applied Energy:
WJ Cong, YT Wang, H Li, Zhen Fang*, J Sun, HT Liu, JT Liu, S Tang, L Xu. Direct production of biodiesel from waste oils with a strong solid base from alkalized industrial clay ash. Applied Energy, 264,114735 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114735.
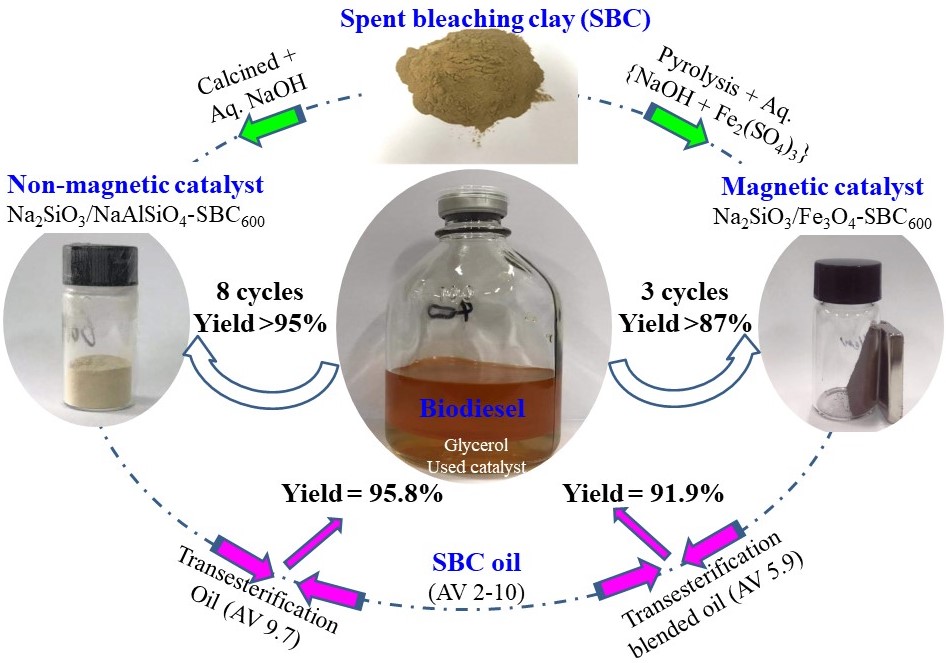
Solid base synthesized from SBC ash for biodiesel production from waste oils with 8 cycles and anti-saponification. It was further magnetized for easy separation.(以废白土为原料合成固体碱,催化废弃油脂制备生物柴油。该催化剂可循环使用8次且可抗皂化,并被进一步磁化为磁性固体催化剂以便于分离。).
以废白土为原料合成固体碱并用于直接催化废弃油脂制备生物柴油
最近,博士生丛文杰(女)在方老师的指导下,在国际学术期刊Applied Energy(IF8.4,Q1)发表以废白土为原料合成固体碱以制备生物柴油的研究性论文。
通过NaOH碱化废白土灰合成固体碱,直接催化废弃油脂制备生物柴油。首先,以大豆油为原料,通过正交试验确定了最优反应条件(醇油比11:1,催化剂量8 wt%,温度65℃,反应3 h),该条件下生物柴油得率为99.1%,该固体碱8次循环后产率仍高于95%。该固体碱可抗皂化,油脂酸值为9.7 mg KOH/g 时生物柴油产率可达96.5%,催化酸值为10的废白土油可得生物柴油产率为95%。此外,进一步通过碳化废白土中的残油作为碳载体和还原剂(将氧化铁转化为四氧化三铁),磁化为磁性固体碱催化剂(6.86 emu/g)。该磁性固体碱催化大豆油制备生物柴油产率为99.2%,经磁性分离后可重复使用3次(生物柴油产率为87%),催化酸值5.9 mg KOH/g的油脂得生物柴油产率为91.9%且未见皂化。本研究充分利用废白土中的无机物(如二氧化硅、氧化铝等),并实现低温下碱催化一步法转化废白土油为生物柴油。整个生产工艺无废弃物生成,并易于应用于工业生产生物柴油。详情可见:
WJ Cong, YT Wang, H Li, Zhen Fang*, J Sun, HT Liu, JT Liu, S Tang, L Xu. Direct production of biodiesel from waste oils with a strong solid base from alkalized industrial clay ash. Applied Energy, 264,114735 (2020), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114735.