A paper was published in Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews
Levoglucosan and Its Hydrolysates via Fast Pyrolysis of Lignocellulose for Microbial Biofuels.
Recently, Dr. LQ Jiang (Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, CAS) and Prof. Zhen Fang, collaborated with Prof. ZL Zhao (Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion), published a review paper in Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews about Fast Pyrolysis for Microbial Biofuels. Fast pyrolysis, which is comparable with the enzyme or acid hydrolysis, should be considered for further development for fermentable levoglucosan (LG) production. This manuscript offers a broad review of the current status and future research perspectives of LG and its hydrolysates production from lignocellulosic biomass by fast pyrolysis for fermentation. The utilization, distribution and formation paths of LG from cellulose are presented.In consideration of the complexity of cellulose structure and lignocellulosic components, the influence of the major individual components (cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and ash) and the structural properties (particle size,degree of polymerization and crystallinity) on the LG formation are reviewed. Aiming to further improve the yield of LG and the fermentability of pyrolysate, a number of pretreatment methods (e.g. hot-water pretreatment,acid pretreatment, acid impregnation) prior to fast pyrolysis, hydrolysis of LG and detoxification before fermentation, and microbial production of valuable products are also discussed in detail. At last, a brief conclusion for the challenge in this topic is provided. The low content of LG and the presentence of inhibitors to biocatalysts in the pyrolysate of lignocelluloses hamper the fermentable utilization of pyrolytic sugars, which need further investigation and improvement to make this process feasible.
Related results were published:
LQ Jiang, Zhen Fang*, ZL Zhao*, AQ Zheng, XB Wang, HB Li, Levoglucosan and Its Hydrolysates via Fast Pyrolysis of Lignocellulose for Microbial Biofuels: A State-of-the-Art Review, Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 105, 215-229 (2019).
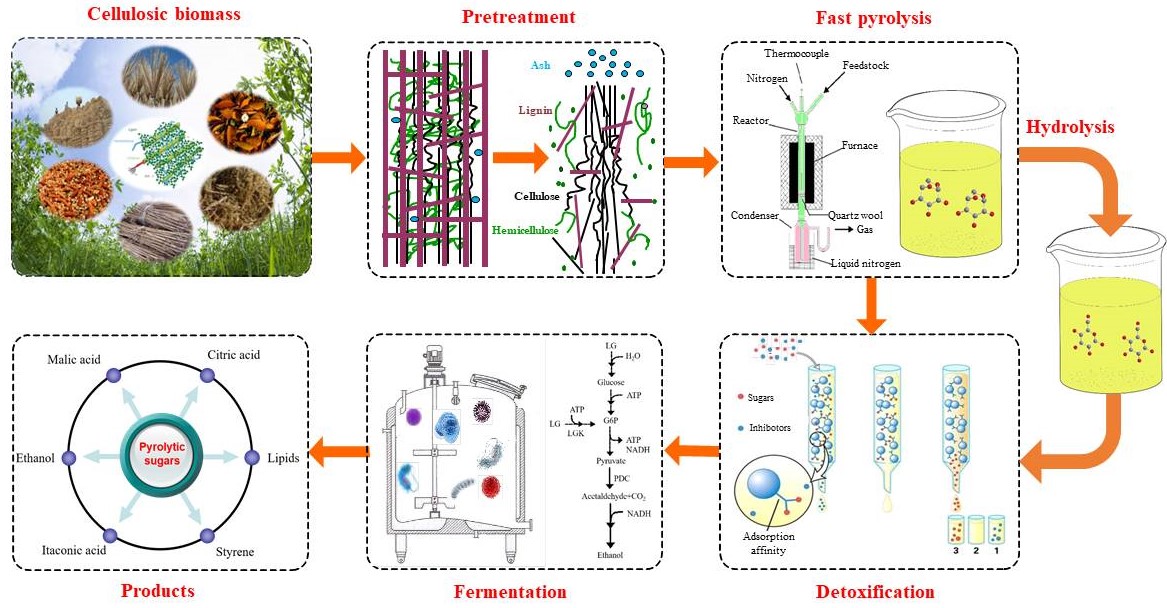
Microbial Biofuels and Chemicals Production via Fast Pyrolysis Routes (通过快速热解途径生产微生物生物燃料和化学品)
———————————————————————-
快速热解木质纤维素生产左旋葡聚糖及其水解产物
最近,蒋丽群博士(中科院广州能源研究所副研究员)为第一作者,方真教授和Zhao ZL研究员(广州能源研究所)共同通讯作者,在期刊《Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews》(IF9.2)上发表了一篇有关于快速热解和发酵生产微生物生物燃料的综述。快速热解,相比较与酶解和酸水解,应考虑热解产物左旋葡聚糖(LG)用于可发酵生产的进一步开发。本论文以广泛的视角对于木质纤维素生物质快速热解,进一步发酵生产左旋葡聚糖及其水解产物的现状和未来研究前景进行了探讨。纤维素的热解产物左旋葡聚糖的应用、分布和形成途径将被说明。考虑到纤维素结构和木质纤维素组分的复杂性,综述了主要组分(纤维素,半纤维素,木质素和灰分)对左旋葡聚糖热解形成的结构性质(粒度,聚合度和结晶度)的影响。为了进一步提高左旋葡聚糖的产量和热解产物的发酵能力,快速热解前会有一些预处理方法(如热水预处理,酸预处理,酸浸渍),左旋葡聚糖水解和发酵前的解毒,以及微生物生产的有价值产品也会详细讨论。最后,提出了关于这个主题挑战的简要结论。左旋葡聚糖的低含量和木质纤维素的热解产物中生物催化剂的抑制剂的存在阻碍了热解糖的可发酵利用的问题,需要进一步研究和改进以使该方法可行。
相关结果发表于:
LQ Jiang, Zhen Fang*, ZL Zhao*, AQ Zheng, XB Wang, HB Li, Levoglucosan and Its Hydrolysates via Fast Pyrolysis of Lignocellulose for Microbial Biofuels: A State-of-the-Art Review, Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 105, 215-229 (2019).