微生物油脂Production of microbial lipid from food wastes with Cryptococcus curvatus
Two-stage process production of microbial lipid by co-fermentation of glucose and N-acetylglucosamine from food wastes with Cryptococcus curvatus
Recently, master student Mr. Jia-xuan Zhang supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article in Bioresource Technology about Two-stage fermentation of food waste (rice and shrimp shells hydrolysates) by Cryptococcus curvatus for lipids.
Microbial lipids were produced through a two-stage process with Cryptococcus curvatus by co-fermenting rice and shrimp shells hydrolysates. The main components of the lipid sample were long-chain fatty acids with carbon chain lengths of 16 and 18, which were similar to those of typical vegetable oils. And the lipid sample showed high potential for biodiesel production. In the shake flask fermentation, co-utilization of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and glucose resulted in improved cell mass and lipid production. The highest cell concentration of 17.60 g/L was achieved in the first-stage, and the highest lipid yield was 0.233 g/g in the second- stage. Scaling up to a 5-L bioreactor increased lipid content to 60.07 % with 0.233 g/g yield. When Cryptococcus curvatus was cultured in the blends of rice hydrolysates and shrimp shells hydrolysate, lipid content and yield were 52.25 % and 0.204 g/g. Co-fermentation of rice hydrolysates and chitin hydrolysate is an effective means for recycling food wastes for lipids.
Related results were published in Bioresource Technology:
JX Zhang, XL Liu, L Wang, Zhen Fang*, Two-stage process production of microbial lipid by co-fermentation of glucose and N-acetylglucosamine from food wastes with Cryptococcus curvatus, Bioresource Technology, 387, 129685, https://doi.org/10,1016/j.biortech.2023.129685 (2023).
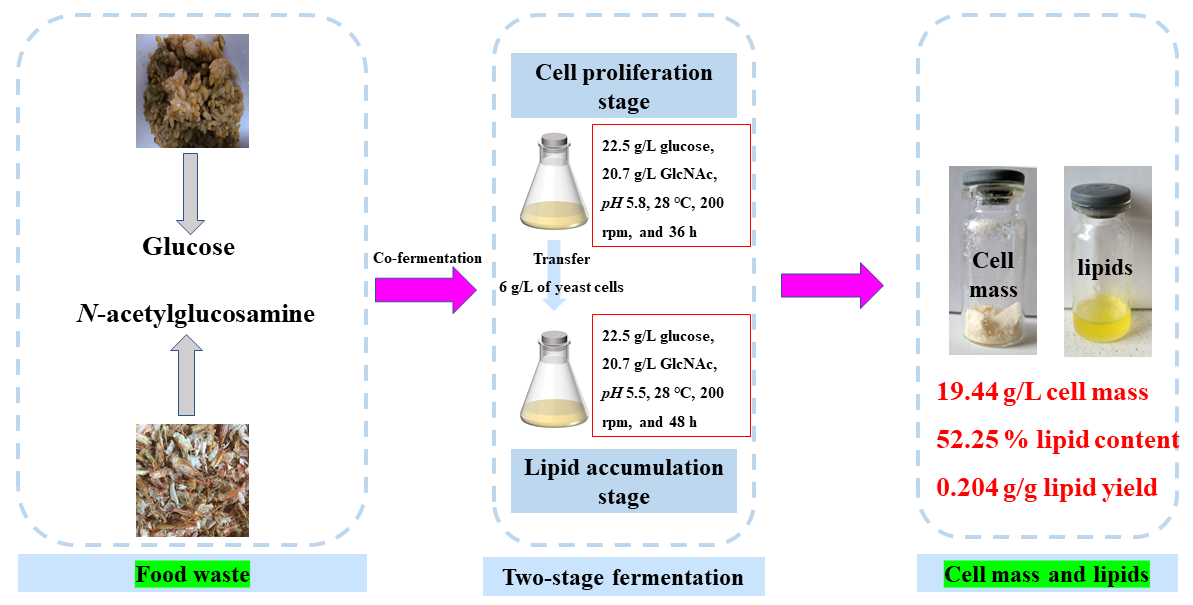
Two-stage process production of microbial lipid by co-fermentation with rice and shrimp shells hydrolysates from food wastes was carried out. After 36 h of the first-stage fermentation, 12.51 g/L of glucose and 9.91 g/L of GlcNAc were consumed simultaneously with 12.18 g/L cell mass produced. Transferring 6 g/L of yeast cells to the second-stage fermentation medium, cell mass of 19.44 g/L, lipid content of 52.25 %, and lipid yield of 0.204 g/g were obtained, respectively. (以食品废弃物中的大米水解物和虾壳的水解物为原料,采用两阶段共发酵工艺生产微生物油脂。在第一阶段发酵36 h后,12.51 g/L 葡萄糖和9.91 g/L N -乙酰氨基葡萄糖被消耗,细胞产量为12.18 g/L。然后将6g/L的酵母细胞转移到第二阶段发酵培养基中。分别获得19.44g/L的细胞质量、52.25%的脂质含量和0.204g/g的脂质产率。
Cryptococcus curvatus共发酵食品废弃物中葡萄糖和N –乙酰氨基葡萄糖两阶段工艺生产微生物脂质
最近,硕士生张家璇(男)在方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Bioresource Technology (Q1, IF 11.4)发表一篇关于两阶段共发酵来自食品废弃物的葡萄糖和N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖生产微生物油脂的研究性论文。
以Cryptococcus curvatus 为研究对象,通过共发酵大米水解物和虾壳的水解物,利用两阶段工艺制备微生物脂质。脂质样品的主要成分是碳链长度为16和18的长链脂肪酸,与典型的植物油相似。脂质样品显示出生产生物柴油的较高潜力。在摇瓶发酵中,N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖(GlcNAc)和葡萄糖的共同利用提高了细胞质量和脂质产量。在第一阶段达到17.60g/L的最高细胞浓度,在第二阶段达到0.233g/g的最高脂质产率。扩大至5-L生物反应器发酵,可将脂质含量提高到60.07%,产量为0.233g/g。Cryptococcus curvatus在大米水解物和虾壳水解物的混合物中培养时,脂质含量和产量分别为52.25%和0.204g/g。大米水解物和甲壳素水解物的联合发酵是回收食品垃圾的有效途径。
结果发表在Bioresource Technology:
JX Zhang, XL Liu, L Wang, Zhen Fang*, Two-stage process production of microbial lipid by co-fermentation of glucose and N-acetylglucosamine from food wastes with Cryptococcus curvatus, Bioresource Technology, 387, 129685, https://doi.org/10,1016/j.biortech.2023.129685 (2023).