Hydrophobic Pd nanocatalysts for one-pot and high-yield production of liquid furanic biofuels at low temperatures
Hydrophobic Pd nanocatalysts for one-pot and high-yield production of liquid furanic biofuels at low temperatures
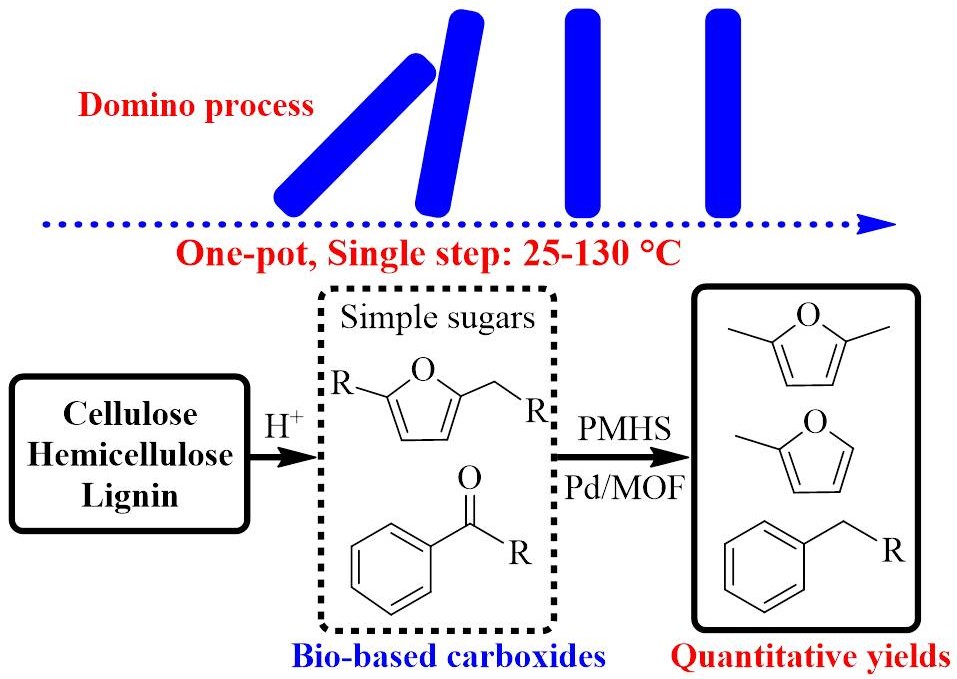
Efficient production of furanic/aromatic hydrocarbons (>95% yields) from biomass derivatives is achieved via a single-step process under mild conditions (25-130 ºC) by using readily available polymethylhydrosiloxane as liquid H-donor over hydrophonic Pd nanoparticles on MOFs.【以聚甲基氢硅氧烷为氢源,在低温条件下 (25-130 ºC),利用疏水纳米钯Pd催化糖类(羰基和羟基化物),一锅高效(> 95% 产量)合成呋喃液体燃料】
Recently, Dr. Hu Li supervised by Prof. Zhen FANG has developed a single-step catalytic process for direct conversion of various saccharides to produce furanic biofuels such as 2,5-dimethylfuran and 2-methylfuran with high yields (> 95%) at 110-130 ºC. The negatively charged hydride (H-) of readily available polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) acting as green H-donor over hydrophobic Pd nanoparticles did not obstruct upstream reactions (e.g., hydrolysis, isomerization and dehydration) for the in situ formation of furanic aldehydes/alcohols from sugars, and could selectively facilitate the subsequent hydrodeoxygenation of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups other than the furanic ring in one pot, as clarified by deuterium-labeling study. Importantly, the unreduced Pd(II) catalysts also exhibited comparable performance in the selective hydrodeoxygenation reaction. Moreover, the catalytic strategy was extended to various carboxides for quantitative production of corresponding furanic/aromatic hydrocarbons at room temperature that were more pronounced than previously reported results, and the optimal Pd/MIL-53(Al) coated with polydimethylsiloxane (Pd/MIL-53(Al)-P) was highly stable with little deactivation and Pd leaching for at least five consecutive cycles.
Related results were published:
1.H Li, W Zhao, Zhen Fang*, Hydrophobic Pd Nanocatalysts for One-Pot and High-Yield Production of Liquid Furanic Biofuels at Low Temperatures, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 215, 18–27 (2017).
2.H Li, W Zhao, A Riisager, S Saravanamurugan*, Z Wang, Zhen Fang*, S Yang*, Pd-catalyzed in-situ domino process for mild and quantitative production of 2,5-dimethylfuran directly from carbohydrates, Green Chemistry, 19, 2101–2106 (2017).
—————————————————————–
高效低温从糖和羰基化物一步直接合成呋喃液体燃料
最近,国际学术期刊Applied Catalysis B: Environmental(影响因子9.4,第一署名单位为南京农业大学,第一作者为博士后李虎,通讯作者为方真教授)及Green Chemistry 【影响因子9.2,第一作者为李虎博士,通讯作者为杨松教授(贵州大学),Saravanamurugan博士(印度)和方真教授】,发表了生物燃料最新研究成果。
该研究团队开发了一个单步催化过程, 以聚甲基氢硅氧烷polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS)为氢源,在低温条件下 (25-130 ºC),利用疏水纳米钯(Pd)催化糖类(羰基和羟基化物),单步高效(> 95% 产量)合成呋喃液体燃料。
他们发现PMHS(带负电荷的高分子氢化物),作为绿色氢源,以纳米钯为催化剂,在原位加氢糖类合成呋喃醛/醇时,不会阻碍其上游的反应 (例如, 水解, 异构化和脱水)。通过同位素氘标记研究证明,该反应系统可以一锅法,有选择地促进羰基和羟基化物的加氢脱氧。更重要的是, 未还原的Pd(II)纳米催化剂在选择性加氢脱氧反应中也表现出相当的性能。此外, 当该催化反应系统扩展到利用各种羰基化物时, 可在室温下,定量生产相应的呋喃/芳烃。用聚二甲基硅氧烷涂层的疏水Pd催化剂具有极高的稳定性, 且在至少连续五个周期中几乎没有失活和Pd浸出。
详情可见:
1.H Li, W Zhao, Zhen Fang*, Hydrophobic Pd Nanocatalysts for One-Pot and High-Yield Production of Liquid Furanic Biofuels at Low Temperatures, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 215, 18–27 (2017).
2.H Li, W Zhao, A Riisager, S Saravanamurugan*, Z Wang, Zhen Fang*, S Yang*, Pd-catalyzed in-situ domino process for mild and quantitative production of 2,5-dimethylfuran directly from carbohydrates, Green Chemistry, 19, 2101–2106 (2017).