High-Concentrated Substrate Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Rice Straw with Glycerol and Aluminum Chloride at Low Cellulase Loadings
High-Concentrated Substrate Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Rice Straw with Glycerol and Aluminum Chloride at Low Cellulase Loadings
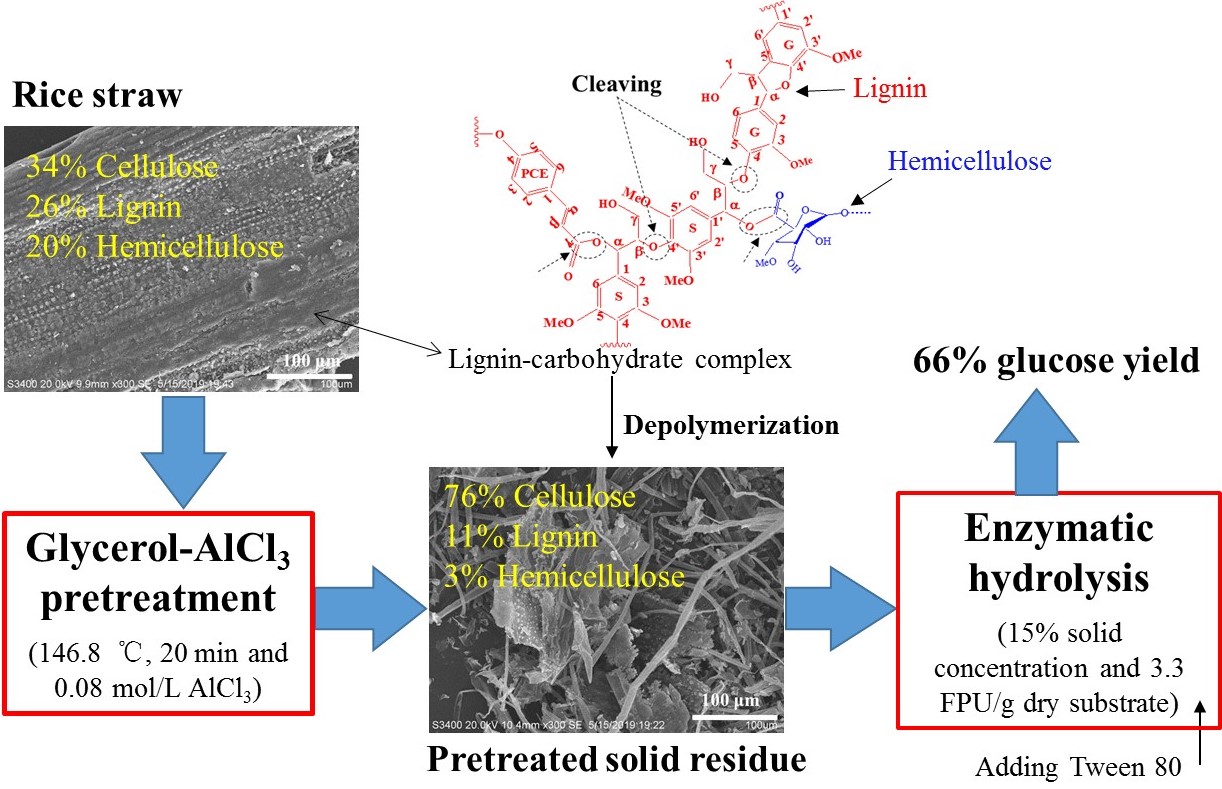
Based on a central composite design, glycerol and AlCl3 pretreated rice straw with 0.08 mol/L AlCl3 at 146.8 °C for 20 min, resulting in 83% delignification, 94% hemicellulose removal, and 92% cellulose recovery for a remarkable glucose yield of 65.7% at high solid loads (15%) and low cellulase loading (3.3 FPU/g dry substrate) with adding Tween 80 (40 mg/g substrate). (通过响应面优化,在146.8 °C和0.08 mol/L AlCl3条件下,水稻秸秆经甘油-氯化铝预处理20 min后,保留92%的纤维素,同时去除83%的木质素和94%的半纤维素;3 FPU/g干基质和15%基质浓度条件下,添加40 mg/g 干基 Tween 80,酶水解48 h,预处理后水稻秸秆的酶解率可达到65.7%。)
Recently, PhD student Mr. Song Tang supervised by Prof. Zhen FANG developed a glycerol and aluminum chloride pretreatment for lignocellulosic biomass. Rice straw was pretreated with glycerol and AlCl3 for enzymatic hydrolysis at low cellulase loadings. Based on a central composite design, 83% delignification, 94% hemicellulose removal, and 92% cellulose recovery (or 76% cellulose in solid residue) were achieved under the optimized pretreatment conditions (0.08 mol/L AlCl3 as catalyst at 146.8 °C for 20 min with 90% glycerol). During glycerol-AlCl3 pretreatment, the lignin-carbohydrate complex was depolymerized, resulting in the complex and recalcitrant construction of straw effectively being destroyed. The enzyme adsorption ability of pretreated straw was 16.5 times that for the original sample. After pretreatment, glucose yield was increased by 2.4 times to 74% for 48 h. Moreover, concentrated solid (15%) with low cellulase loading (3.3 FPU/g dry substrate) achieved 58.6% glucose yield, and further increased by 12% to 65.7% by adding Tween 80.
The results were published:
S Tang, Q Dong, Zhen Fang*, WJ Cong, ZD Miao, High-Concentrated Substrate Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Rice Straw with Glycerol and Aluminum Chloride at Low Cellulase Loadings, Bioresource Technology, 294, 122164 (2019).
————————————-
甘油和氯化铝预处理水稻秸秆用于低纤维素酶载量条件下高基质浓度酶水解
最近,博士生唐松(男)同学在方老师的指导下,开发出一种应用于木质纤维素生物质的甘油-氯化铝预处理技术,其对木质纤维素组分分离具有极好的选择性。通过响应面优化,水稻秸秆在146.8 °C和0.08 mol/L AlCl3条件下,处理20 min后,92%的纤维素被保留,83%的木质素和94%的半纤维素被去除。同时,固体残渣中纤维素含量达到76%。在甘油-AlCl3预处理过程中,木质素-碳水化合物形成的复合物被解聚,导致秸秆复杂和顽固的结构被有效地破坏。水稻秸秆经预处理后,对纤维素酶的吸附能力提高了16.5倍,酶解率较原始水稻秸秆提高2.4倍,达到了74%。此外,在3 FPU/g和15%基质浓度条件下,酶水解48 h,预处理后水稻秸秆的酶解率达到58.6%,且添加40 mg/g 干基 Tween 80后,提高了12%,达到65.7%。
结果发表在Bioresource Technology:
S Tang, Q Dong, Zhen Fang*, WJ Cong, ZD Miao, High-Concentrated Substrate Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Rice Straw with Glycerol and Aluminum Chloride at Low Cellulase Loadings, Bioresource Technology, 294, 122164 (2019).