微生物油脂Efficient lignin removal from rice straw via alkaline-freeze combined with hydrothermal pretreatment to obtain high-titer sugar for microbial lipid production
星期六, 10 1 月, 2026Efficient lignin removal from rice straw via alkaline-freeze combined with hydrothermal pretreatment to obtain high-titer sugar for microbial lipid production
Recently, PhD student Miss Dong Qian supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang published a research article in Biomass and Bioenergy (Q2, Impact Factor: 5.8) about microbial lipid production from rice straw.
This study developed an integrated process for converting rice straw into microbial lipids. The straw was first pretreated using alkali‑freeze combined with hydrothermal method, followed by high‑solid enzymatic hydrolysis to produce fermentable sugars for lipid fermentation. Alkali‑freeze combined with hydrothermal pretreatment had an extremely good selectivity for component fractionation, resulting in 86.9% delignification, and 97.1% cellulose recovery, 78.8% hemicellulose recovery. After hydrolysis, glucose and xylose yield of pretreated straw reached 91.1% and 68.9%, respectively. Further optimization with response surface methodology increased the yields to 100% for glucose and 81.1% for xylose. Fed‑batch saccharification was applied under low enzyme loading (10 FPU/g cellulase, 20% solid loading), producing 111.4 g/L glucose and 36.3 g/L xylose, with corresponding yields of 83.4% and 66.3%. Using the mixed sugars, cultivation conditions for Cryptococcus curvatus were optimized, achieving a lipid concentration of 6 g/L and a yield of 0.175 g/g. Adding Tween 80 increased these to 7.7 g/L and 0.21 g/g, respectively. Finally, the hydrolysates were separated for lipid fermentation, producing 7.3 g/L lipids with a yield of 0.198 g/g. This work provides a promising strategy for the conversion and utilization of agricultural straw.
Related results were accepted in Biomass and Bioenergy:
Q Dong, S Tang*, Zhen Fang*,Efficient lignin removal from rice straw via alkaline-freeze combined with hydrothermal pretreatment to obtain high-titer sugar for microbial lipid production. Biomass and Bioenergy 2026, 209, 108933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2026.108933
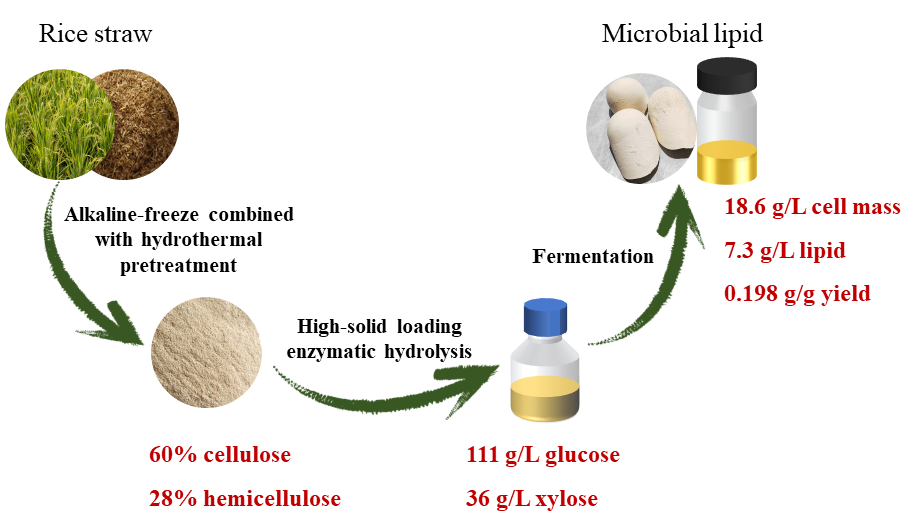
Microbial lipid production from pretreated rice straw hydrolysates (水稻秸秆经碱冷冻结合水热预处理后,分批补料酶解,将水解产物作为碳源,通过弯曲隐球菌高效生产油脂)
水稻秸秆经碱冷冻结合水热预处理后,通过弯曲隐球菌高效生产油脂
最近,博士生董倩在方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Biomass and Bioenergy (Q2; Impact factor: 5.8)上发表了一篇关于利用水稻秸秆产微生物油脂的研究性论文。
通过碱冷冻结合水热预处理和高固载酶解,从水稻秸秆中获取高浓度可发酵性糖,为微生物油脂发酵提高优质碳源。首先,通过单因素实验确定最佳预处理条件,在此条件下,纤维素和半纤维素收率分别为97.1%和78.8%,木质素去除率为86.9%。预处理秸秆经酶解后,葡萄糖和木糖产率分别达到91.1%和68.9%。随后,通过响应面优化酶解条件,葡萄糖和木糖产率分别提高至100%和81.1%。在此基础上,通过分批补料实现预处理秸秆在低酶载量下的高浓糖化 (10 FPU/g纤维素酶,20%固载量),获得111.4 g/L葡萄糖和36.3 g/L木糖,对应产率分别为83.4%和66.3%。最后,通过单因素实验确定弯曲隐球菌发酵混糖 (葡萄糖和木糖) 产油脂条件,在最佳条件下,总油脂量为6 g/L,油脂产率达到0.175 g/g,在培养基中添加吐温80,总油脂量和油脂产率分别提高至7.7 g/L和0.21 g/L。基于该培养条件,将预处理秸秆水解产物作为碳源培养油脂酵母,产出油脂7.3 g/L,其产率达到0.198 g/g。本研究为农作物秸秆的转化利用提供了新思路。
结果发表在Biomass and Bioenergy:
Q Dong, S Tang*, Zhen Fang*,Efficient lignin removal from rice straw via alkaline-freeze combined with hydrothermal pretreatment to obtain high-titer sugar for microbial lipid production. Biomass and Bioenergy 2026, 209, 108933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2026.108933