焦耳加热Joule heating for carbon material Synthesis: Mechanisms, material evolution, and sustainable prospects
星期四, 9 10 月, 2025Joule heating for carbon material Synthesis: Mechanisms, material evolution, and sustainable prospects
Recently, under the supervision of Associate Professor Wei Chen, master’s student Miss Zijun Pan published a review article titled “Joule heating for carbon material Synthesis: Mechanisms, material evolution, and sustainable prospects” in an international academic journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.
This comprehensive review systematically explores the research progress and application potential of Joule heating as an emerging electrothermal technique for carbon material synthesis. By integrating multiple perspectives—including material synthesis, mechanistic simulation, and sustainability assessment-the article highlights the highly efficient tunability of Joule heating in the preparation of various carbon materials such as graphitic carbon, flash graphene, and carbon nanotubes, and elaborates on heteroatom-doping and metal-loading functionalization strategies. Furthermore, by combining machine learning and multiscale simulations, the study elucidates the structural evolution mechanisms of materials under extreme thermal conditions. Through life-cycle assessment (LCA), it also verifies the remarkable economic and environmental advantages of this technique, providing a theoretical foundation and technological pathway for the green manufacturing of carbon materials.
The results were published in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews:
Pan Z, et al. Joule heating for carbon material synthesis: Mechanisms, material evolution, and sustainable prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2026, 116290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2025.116290
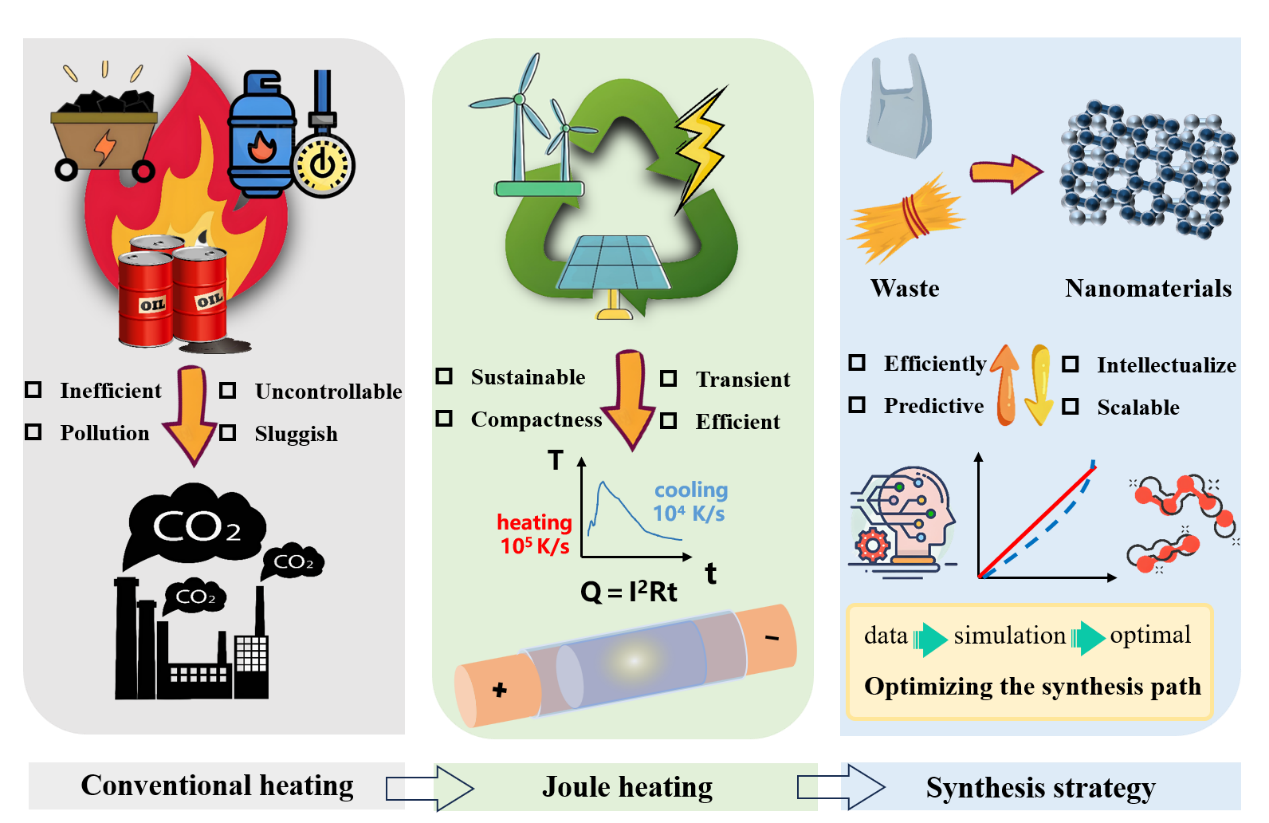
Joule heating for carbon material Synthesis
焦耳加热合成碳材料:机理、演化与可持续前景
最近,生物能源组硕士生潘子君在陈伟副教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (Q1, IF=16.3) 发表了一篇题为焦耳加热合成碳材料:机理、演化与可持续前景的综述论文。
本综述系统探讨了焦耳加热作为一种新兴电热技术在碳材料合成中的研究进展与应用潜力。通过整合材料合成、机理模拟与可持续性评估等多维度内容,文章重点分析了焦耳加热在石墨碳、闪蒸石墨烯、碳纳米管等多种碳材料制备中的高效调控能力,并阐述了其在杂原子掺杂与金属负载方面的功能化策略。研究进一步结合机器学习与多尺度模拟揭示了极端热条件下材料结构的演化机制,并通过生命周期评估验证了该技术在经济性与环境友好性方面的显著优势,为推动碳材料绿色制造提供了理论依据与技术路径。
结果发表在Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews:
Pan Z, et al. Joule heating for carbon material synthesis: Mechanisms, material evolution, and sustainable prospects. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 2026, 116290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2025.116290