炭催化热解Realizing the Co-valorization of Waste Cooking Oil into High-quality Biofuel and Carbon Nanotube Precursor via Catalytic Pyrolysis Process
星期一, 18 3 月, 2024Realizing the Co-valorization of Waste Cooking Oil into High-quality Biofuel and Carbon Nanotube Precursor via Catalytic Pyrolysis Process
Recently, Master student Mr. Guo-qiang Zhu supervised by Associate Prof. Lu-jiang Xu published a research article in Chemical Engineering Journal about realizing the co-valorization of waste cooking oil into high-quality biofuel and carbon nanotube precursor via catalytic pyrolysis process.
Valorizing renewable precursors into high-quality biofuel and functional carbon nanomaterials can considerably improve the economic viability. Here, we propose a process for integrated production of high-quality biofuel and carbon nanotubes from waste cooking oil via catalytic pyrolysis coupling with CVD technology. The natural biochar catalyst demonstrates excellent deoxygenation performance and good stability in catalytic pyrolysis process. The AAEMs content in biochar catalysts from various sources has a strong correlation with the selectivity of esters and hydrocarbons in bio-oil. The biofuel obtained under optimal conditions exhibited potential as a precursor for jet fuel. The combined CVD process successfully convert pyrolysis gas into multi-wall carbon nanotubes with yield of 2.13%. The technical-economic analysis demonstrated the feasibility of the integrated production process, projecting profitability and substantial total profit over a ten-year period. Overall, this study improves the economic viability of the waste cooking oil pyrolysis process and can support its wider commercial application.
Related results were published in Chemical Engineering Journal:
GQ Zhu, MX Zhu, EZ Wang, CX Gong, YR Wang, WJ Guo, GL Xie, W Chen, C He, LJ Xu*, H Li, Y Zhang, Zhen Fang, Natural Biochar Catalyst: Realizing the Co-Valorization of Waste Cooking Oil into High-Quality Biofuel and Carbon Nanotube Precursor via Catalytic Pyrolysis Process, Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 16.7), 486 (2024), 150195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.150195.
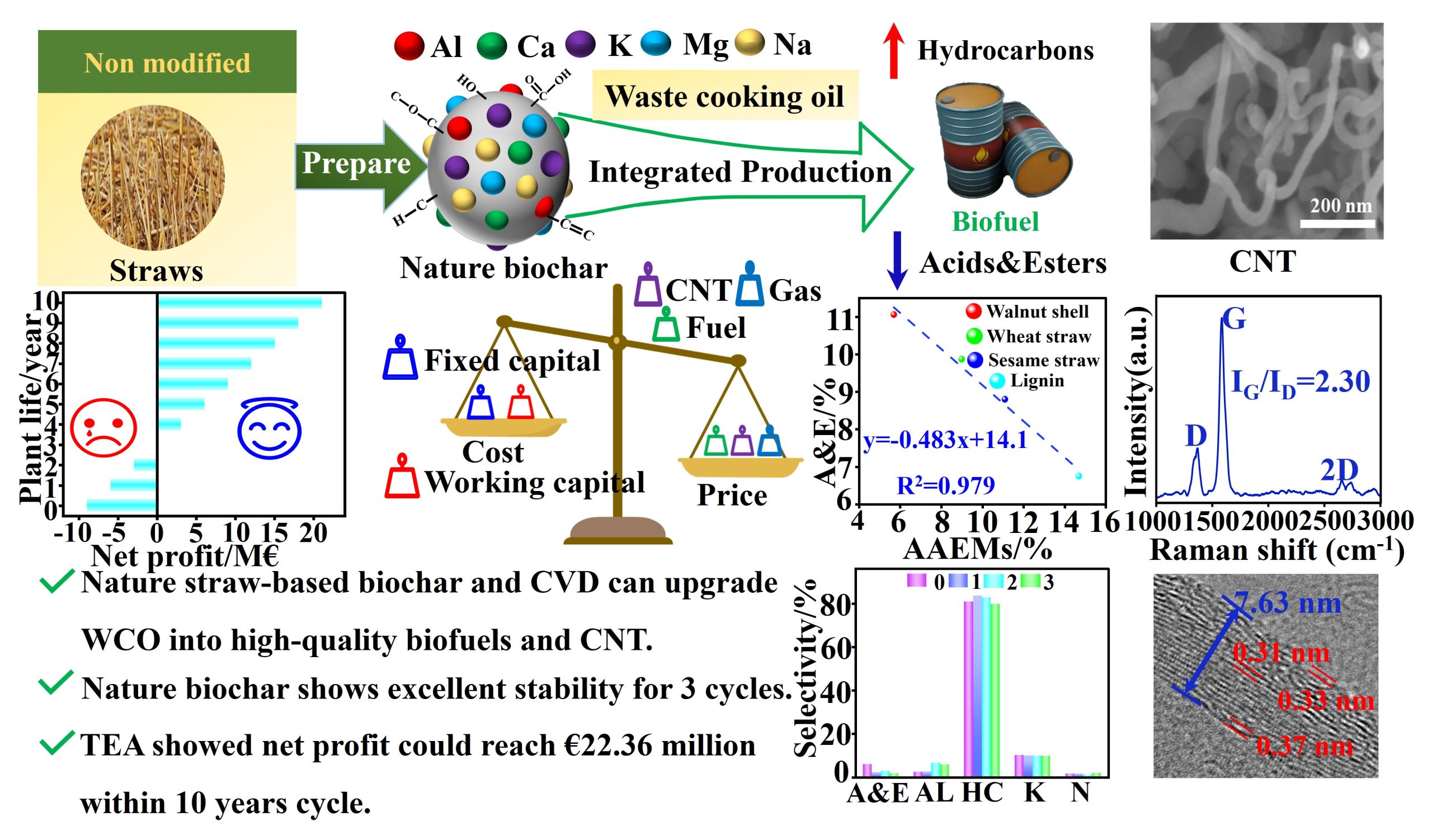
Co-valorization of waste cooking oil into high-quality biofuel and carbon nanotube precursor via catalytic pyrolysis process催化热解工艺实现餐厨废油共价制备优质生物燃料和碳纳米管前驱体
催化热解工艺实现废食用油转化为优质生物燃料和碳纳米管前驱体
最近,硕士生祝国强在徐禄江副教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Chemical Engineering Journal (Q1, IF=15.1) 发表了一篇关于原生生物炭热解催化废弃油脂联产高品质液体燃料和碳纳米管前驱体的研究性论文。
以废弃油脂为原料联产高品质液体燃料和功能性碳纳米材料可显著提高经济可行性。因此,本文提出了一种利用秸秆基生物炭催化热解耦合气相沉积技术联产生产高质量生物燃料和碳纳米管工艺。原生生物炭在催化热解过程中表现出优异的脱氧性能和良好的稳定性。不同来源的生物炭催化剂中碱金属含量与热解油中酯类和烃类的选择性呈一阶线性相关。在最佳条件下获得的生物燃料表现出作为航空燃料前体的潜力。气相沉积技术成功实现将热解气转化为多壁碳纳米管,收率为2.13%。技术经济评价证明了联产的可行性,并预测了10年期间的盈利能力。本研究提高了废弃油脂热解工艺的经济可行性,为其更广泛的商业应用提供了参考。
结果发表在Chemical Engineering Journal:
GQ Zhu, MX Zhu, EZ Wang, CX Gong, YR Wang, WJ Guo, GL Xie, W Chen, C He, LJ Xu*, H Li, Y Zhang, Zhen Fang, Natural Biochar Catalyst: Realizing the Co-Valorization of Waste Cooking Oil into High-Quality Biofuel and Carbon Nanotube Precursor via Catalytic Pyrolysis Process, Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 16.7), 486 (2024), 150195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.150195.