液化塑料和竹粉制烃In-situ hydrogen generation and hydrodeoxygenation via Ni-Mo alloy tandem catalysis: Co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels
In-situ hydrogen generation and hydrodeoxygenation via Ni-Mo alloy tandem catalysis: Co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels
Recently, PhD student Mr. Sheng-ren Li, supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang, published a research article on the co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels.
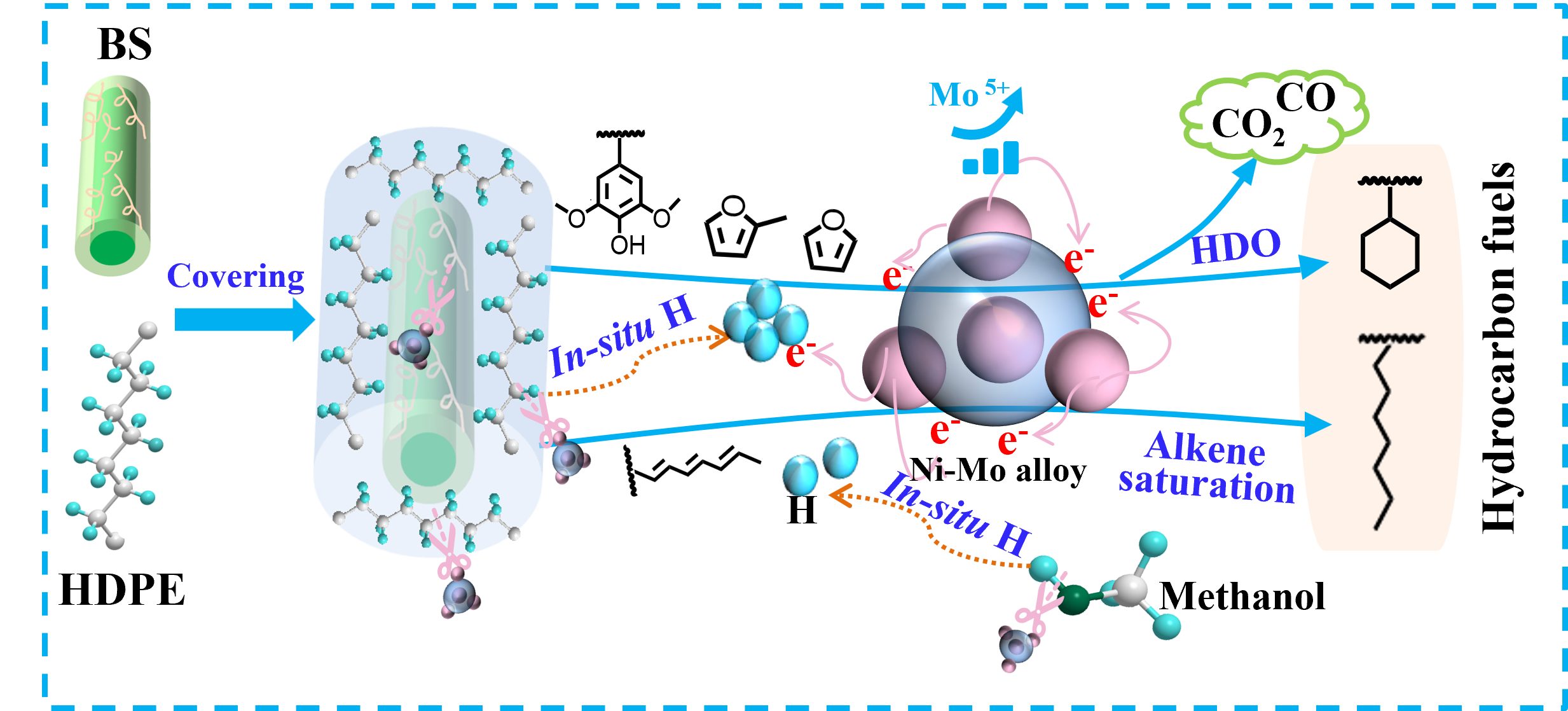
This study reports a Ni-Mo/SiO2 alloy tandem catalysis in-situ hydrogen generation and hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) reaction, upgrading of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and bamboo sawdust (BS) into hydrocarbons (HCs, C6-C24) in methanol. HCs achieved a 35.81 wt% yield and 95.73% selectivity (95.42% alkanes), approximating the composition of commercial diesel. HDPE and methanol as dual hydrogen sources, with hydrogen from HDPE used for HDO and hydrogen from methanol for alkene saturation. Furthermore, kinetic studies and SEM revealed that BS covered by molten HDPE avoided attacks by methanol at low temperatures (< 360 °C) to reach simultaneous decomposition with HDPE, ensuring the continuity of hydrogen generation and deoxygenation. H2-TPR, XRD, TEM, and EDS confirmed that the catalyst formed an alloy structure that facilitated hydrogen generation (H2 increased from 0.27 to 3.90 mol/kg) and activation and adsorption of H2. XPS revealed that abundant and dynamic cycling Mo5+ on Ni-Mo/SiO2 formed numerous oxygen vacancies (OV/OL = 1.78) as active sites for deoxygenation reactions, promoting crude oil deoxygenation (CO2 increased from 0.17 to 3.28 mol/kg). This ensured high HC selectivity (≥ 90%) in crude oil after five cycles. This tandem catalysis presents a pathway for the energy conversion of plastic and biomass waste.
Related results were accepted in Renewable Energy:
SR Li, N Ji, S Yong, LJ Xu, JA Kozinski, Zhen Fang*, In-situ hydrogen generation and hydrodeoxygenation via Ni-Mo alloy tandem catalysis: Co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels, Renewable Energy, 206 (2026), 125224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2026.125224.
Co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels with Ni-Mo alloy catalysis. Ni-Mo合金催化聚乙烯和竹屑共液化制烃类燃料
——————————————————————————————————————————————-
Ni-Mo合金串联催化原位制氢和加氢脱氧:高密度聚乙烯和竹屑共液化制烃类燃料
近期,博士生李胜任在方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Renewable Energy (Q1; Impact factor: 9.1)发表了一篇关于高密度聚乙烯和竹屑共液化制烃的研究性论文。
研究报道Ni-Mo/SiO2合金串联催化原位制氢和加氢脱氧(HDO)反应,在甲醇中将高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)和竹屑(BS)提质为烃(HCs, C6-C24)。HCs实现了35.81wt%的产率和95.73 %的选择性(95.42 %的烷烃),接近商业柴油的组成。HDPE和甲醇作为双氢源,来自HDPE的氢气用于HDO,来自甲醇的氢气用于烯烃饱和。此外,动力学研究和SEM显示,被熔融HDPE覆盖的BS在低温(< 360♀C)下避免了甲醇的侵蚀,从而与HDPE同时分解,确保了产氢和脱氧的连续性。H2-TPR、XRD、TEM和EDS证实催化剂形成了促进氢气产生(H2从0.27增加到3.90 mol/kg)和H2活化和吸附的合金结构。XPS表明,在Ni-Mo/SiO2上丰富的动态循环Mo5+形成了大量的氧空位(OV/OL = 1.78)作为脱氧反应的活性中心,促进了原油脱氧(CO2从0.17增加到3.28 mol/kg)。这确保了五次循环后原油中的高HC选择性(≥90 %)。这种串联催化为塑料和生物质废物的能量转化提供了途径。
结果发表在Renewable Energy:
SR Li, N Ji, S Yong, LJ Xu, JA Kozinski, Zhen Fang*, In-situ hydrogen generation and hydrodeoxygenation via Ni-Mo alloy tandem catalysis: Co-liquefaction of high-density polyethylene and bamboo sawdust into hydrocarbon fuels, Renewable Energy, 206 (2026), 125224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2026.125224.