光电化学转化木质素Interfacial high-valence Ni(IV)-enabled C-H activation for photoelectrochemical C-C bond cleavage of lignin to exclusively produce aromatic carboxylic acids
Interfacial high-valence Ni(IV)-enabled C-H activation for photoelectrochemical C-C bond cleavage of lignin to exclusively produce aromatic carboxylic acids
Recently, PhD student Mr. Pei-dong Wu supervised by Profs. Hu Li and Zhen Fang published a research article in Chemical Engineering Journal about photoelectrochemical C-C bond cleavage of lignin to exclusively produce aromatic carboxylic acids.
Sustainable upgrading of biomass to high-value chemicals is greatly dependent on catalytic C-C/C-O bond cleavage of high selectivity. Here, an oxidation-enhanced photoelectrochemical protocol was developed to be capable of breaking different types of C-C bonds for efficiently producing aromatic carboxylic acids (85.0-99.8% yields) from lignin. Ni local electronic state of the prepared F-Fe2O3-Co:NiOxHy with excellent durability could be modulated, and high-valence Ni(Ⅳ) reactive species played a key role in the oxidative C-C bond scission of various lignin models. In-situ characterization and control experiments indicated that photocatalytic radical and electrocatalytic interface facilitated C-H/O-H delocalization, contributing significantly to the enhanced oxidation process. In addition, quantum calculations elaborated that photo-excited holes and Ni(Ⅳ) are key reactive species for enhancive electrocatalytic cleavage of different C-C bonds in lignin to exclusively furnish aromatic carboxylic acids. This research provides a renewable funnel strategy for using solar energy to produce high-value mono-functional products from biomass.
Related results were accepted in Chemical Engineering Journal:
PD Wu, LY Li, Hu Li *, Zhen Fang *, Interfacial high-valence Ni(IV)-enabled C-H activation for photoelectrochemical C-C bond cleavage of lignin to exclusively produce aromatic carboxylic acids, 2024, 490, 151722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.151722.
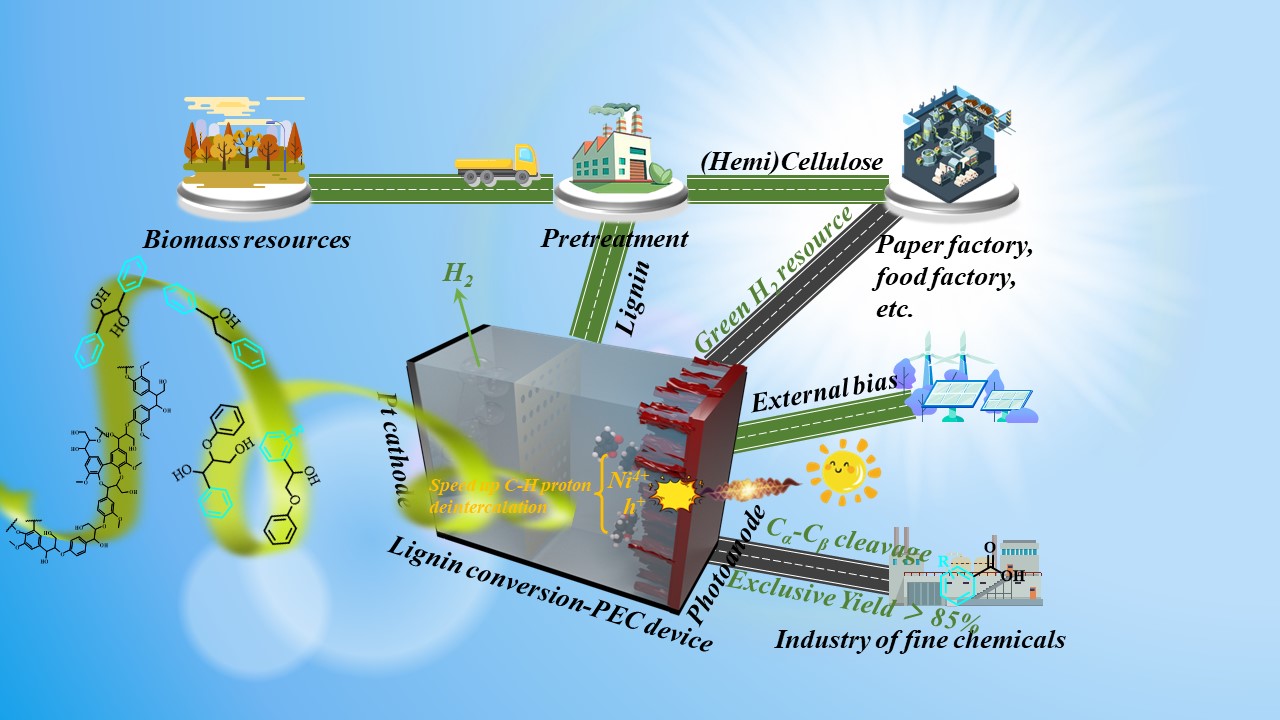
A “funnel” type strategy for photoelectrochemical lignin high value utilization. 用于光电化学木质素高值化利用的“漏斗”型策略。
博士生吴培栋在李虎教授和方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Chemical Engineering Journal发表论文:
界面高价镍(IV)C-H活化促光电化学C-C键裂解木质素专一生产芳香族羧酸
最近,博士生吴培栋在李虎教授和方真教授的指导下,在国际学术期刊Chemical Engineering Journal (Q1; Impact factor: 15.1)上发表了一篇关于光电化学C-C键裂解木质素专一生产芳香族羧酸的论文。
生物质向高价值化学品的可持续升级在很大程度上依赖于C-C/C-O键的高选择性催化裂解。在此,我们开发了一种氧化增强型光电化学方案,该方案能够断裂不同类型的C-C键,从而高效地从木质素中生产出芳香族羧酸(产率为 85.0%-99.8%)。所制备的F-Fe2O3-Co:NiOxHy光电极具有优异的耐久性,其Ni局部电子态可被调控,高价态Ni(Ⅳ)活性物种在各种木质素模型的C-C键氧化裂解过程中发挥了关键作用。原位表征和对照实验表明,光催化自由基和电催化界面促进了C-H/O-H质子脱出,对氧化过程的增强起了重要作用。此外,DFT计算表明,光激发空穴和Ni(Ⅳ)是增强电催化木质素衍生物C-C键裂解的关键活性物种,使其可完全转换为芳香族羧酸。这项研究为利用太阳能从生物质中生产高价值单功能产品提供了一种可再生“漏斗”策略。
详情可见:
PD Wu, LY Li, Hu Li *, Zhen Fang *, Interfacial high-valence Ni(IV)-enabled C-H activation for photoelectrochemical C-C bond cleavage of lignin to exclusively produce aromatic carboxylic acids, 2024, 490, 151722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.151722.