生物质锌-空气电池Biochar-Based Oxygen Electrocatalysts for Advanced Zn-Air Batteries: Mechanisms, Applications, and Prospects
20 1 月, 2026Biochar-Based Oxygen Electrocatalysts for Advanced Zn-Air Batteries: Mechanisms, Applications, and Prospects
Recently, under the supervision of Professor Zhen Fang, collaborated with Profs. Janusz Kozinski (Lakehead Univ, Canada) and Roger Ruan (Minnesota Univ, USA), PhD student Miss Xiao-ru Meng published a review article focusing on the regulated fabrication of biochar-based oxygen electrocatalysts for zinc-air batteries in Chemical Engineering Journal.
Biochar is a biogenic carbon material with abundant sources and superior performance. The preparation of functional biochar with specific structures (such as quantum dots, nanofibers, hierarchical porous structures) from biomass materials holds substantial scientific significance for the field of electro-catalysis. This article depicts the unique advantages inherent to various types of biomass, exploring the potential applications of derived biochar for oxygen electro-catalysts. This may offer new solutions to the issues of high costs and scarce resources associated with traditional precious metal catalysts. The structural diversity and molecular tunability of biomass make it an ideal raw material for the preparation of three-dimensional, functional, self-doped, and self-assembled carbon materials. This review is organized around the core framework of a “bidirectional regulation” strategy: First, on the forward path, it systematically outlines the various methods of transforming biomass into functional biochar and delves into the mechanisms by which the inherent structure and composition of biomass precursors affect the performance of derived biochar. Then, on the reverse path, it focuses on how to reverse-engineer and optimize the material properties of biochar guided by the target oxygen electro-catalytic performance, thus constructing a rational design loop from performance requirements to precursor selection. This review provides theoretical guidance for the preparation of biochar-based oxygen electro-catalysts, and also offers a new perspective on the preparation of carbon materials based on biomass.
Results were published in Chemical Engineering Journal:
XR Meng, S Gao, Janusz A. Kozinski, Roger Ruan, Zhen Fang*, Biochar-based oxygen electrocatalysts for advanced Zn-air batteries: Mechanisms, applications, and prospects, Chemical Engineering Journal, 529 (2026), 172878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2026.172878.
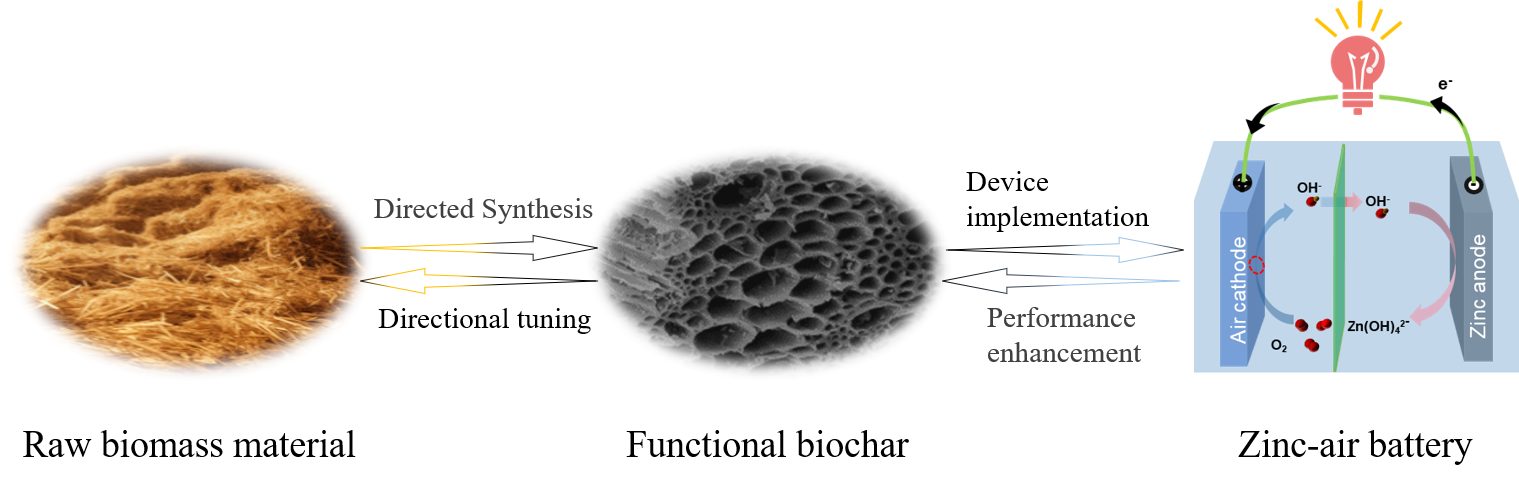
Mutual biomass-biochar modulation engineered for oxygen electrocatalysts in zinc-air batteries用于锌 – 空气电池氧电催化剂的生物质 – 生物炭协同调控工程
用于先进锌空气电池的生物炭基氧电催化剂:机制、应用与展望
最近,在方真教授的指导下,与加拿大湖首大学Janusz Kozinski院士和美国明尼苏达大学阮榕生院士合作,博士生孟晓茹在《Chemical Engineering Journal》上发表了一篇关于调控制备生物炭氧电催化剂,用于锌空气电池的综述文章。
生物炭是一种具有丰富来源且性能优异的生物碳材料。从生物质材料制备具有特定结构(如量子点、纳米纤维、层级多孔结构)的功能性生物炭,对电催化领域具有重要的科学意义。本文阐述了各种生物质类型固有的独特优势,探讨衍生生物炭在氧电催化剂中的潜在应用。这可能为传统贵金属催化剂所带来的高成本和资源稀缺问题提供新的解决方案。生物质的结构多样性和分子可调性使其成为制备三维、功能性、自掺杂和自组装碳材料的理想原料。本综述围绕“双向调控”策略的核心框架展开:首先,在前瞻路径上,系统地概述了将生物质转化为功能性生物炭的各种方法,并深入探讨生物质前体固有结构和组成如何影响衍生生物炭性能的机制。然后,在相反的路径上,它聚焦于如何逆向工程并优化生物炭的材料性质,并以目标氧电催化性能为指导,从而构建一个从性能要求到前驱体选择的合理设计循环。本综述为基于生物炭的氧电催化剂的制备提供了理论指导,同时也为基于生物质制备碳材料提供了新的视角。
结果发表在Chemical Engineering Journal:
XR Meng, S Gao, Janusz A. Kozinski, Roger Ruan, Zhen Fang*, Biochar-based oxygen electrocatalysts for advanced Zn-air batteries: Mechanisms, applications, and prospects, Chemical Engineering Journal, 529 (2026), 172878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2026.172878.