水热制氢Hydrogen production from biomass via hydrothermal gasification using Ni-Ce catalysts supported on Kaolin
16 11 月, 2025Hydrogen production from biomass via hydrothermal gasification using Ni-Ce catalysts supported on Kaolin
Recently, PhD student Mr. Zhi-qiang Wang supervised by Prof. Zhen Fang, collaborated with Dr. Sonil Nanda (Dalhousie University) and Prof. Janusz A Kozinski (Lakehead University) published a research article in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy about Hydrogen production from biomass via hydrothermal gasification using Ni-Ce catalysts supported on Kaolin.
The development of efficient and stable catalysts for the effective gasification of biomass waste is crucial for advancing renewable hydrogen production. In this study, a Ni–Ce bimetallic catalyst supported on calcined kaolin (Ni–Ce/c-Kaolin) was prepared via co-impregnation and applied to the supercritical water gasification of cotton stalks at 340–400 °C and 16–30 MPa. Under the optimized conditions (380 °C, 5 min, 0.5 g cotton stalks, and 0.5 g catalyst), the H2 yield increased from 1.85 to 21.82 mmol/g, and the specific surface area rose from 4.74 to 26.46 m²/g; the introduction of 2.5 wt% Ce further enhanced catalytic activity, achieving an H2 yield 2.25 times higher than that of Ni/c-Kaolin. The addition of Ce altered the reduction behavior and electronic structure of Ni; XPS analysis indicated that the Ce3+/Ce4+ redox cycle promoted oxygen mobility, while TGA and FT-IR results revealed that Ce suppressed carbon deposition and facilitated the participation of surface hydroxyl groups in the reaction. Gasification experiments with different crop residues showed that cotton stalks exhibited the highest gasification efficiency (70.06%) and H2 yield (21.82 mmol/g), surpassing those of rice and wheat straw. Ni–Ce/c-Kaolin catalyst retained high catalytic activity and structural stability after undergoing recycling tests. This work reveals a new route for the high-value utilization of agricultural residues, while also confirming the potential of kaolin as an alternative to conventional alumina supports.
Results were published in International Journal of Hydrogen Energy:
ZQ Wang, S Nanda, GX Xu, JA. Kozinski, Zhen Fang*, Hydrogen production from biomass via hydrothermal gasification using Ni–Ce catalysts supported on Kaolin, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 193 (2025), 152353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2025.152353
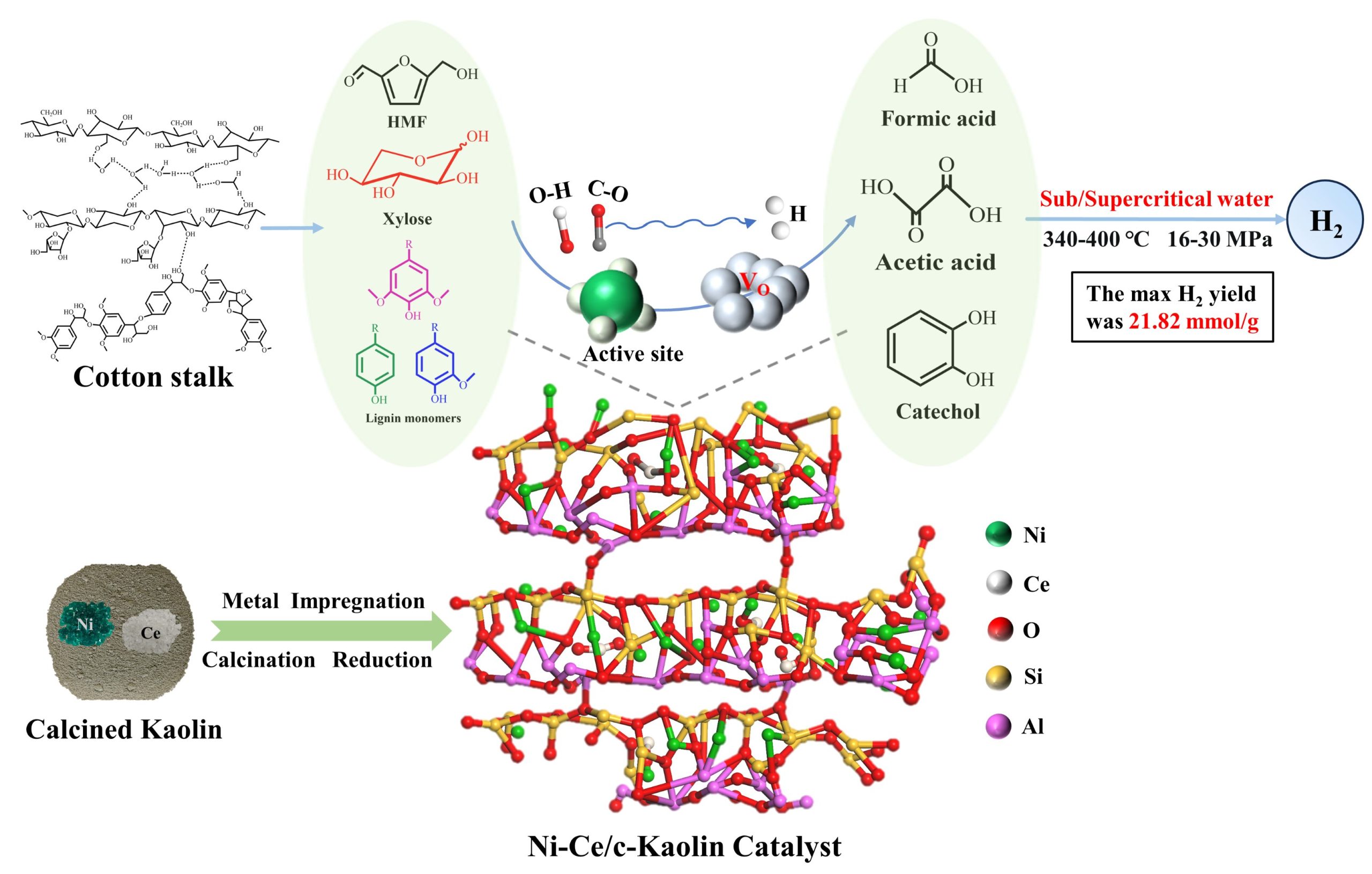
Kaolin supported Ni-Ce catalyst for hydrothermal gasification of cotton stalk at 380 ℃ with 83.9% H2 yield. 高岭土负载Ni-Ce催化剂水热气化生物质制氢研究
——————————————– ————————————————————————–
高岭土负载Ni-Ce催化剂水热气化生物质制氢研究
最近,在方真教授的指导下,博士生王志强先生与加拿大Dalhousie大学助理教授Sonil Nanda博士和加拿大Lakehead 大学工学院院长Janusz A Kozinski院士合作,在《国际氢能杂志》上发表了一篇关于利用高岭土负载的Ni-Ce催化剂通过水热气化生物质制氢的研究文章。
开发高效稳定的催化剂用于生物质废弃物的有效气化对于推进氢气的生产至关重要。本研究采用共浸渍法制备了负载于煅烧高岭土上的Ni-Ce双金属催化剂(Ni-Ce/c-Kaolin),并将其应用于棉秆在340–400 °C和16–30 MPa 条件下的超临界水气化。在优化条件下(380 °C,5 min,0.5 g棉秆,0.5 g催化剂),H2产率从1.85 mmol/g 提高到21.82 mmol/g,比表面积从4.74 m²/g增加到26.46 m²/g;引入2.5 wt%的Ce进一步提高了催化活性,H2产率比Ni/c-Kaolin 提高了2.25倍。Ce的加入改变了Ni的还原行为和电子结构;XPS分析表明Ce3+/Ce4+氧化还原循环促进了氧的迁移,而TGA和FT-IR结果表明Ce抑制了积碳,并促进了表面羟基参与反应。不同农作物残渣的气化实验表明,相较于稻草和麦秸,棉秆的气化效率最高(70.1%),H2产率也最高(21.82 mmol/g)。Ni–Ce/c-Kaolin催化剂在循环使用后仍保持了较高的催化活性和结构稳定性。这项工作揭示了农业残渣高价值利用的新途径,同时也证实了高岭土作为传统氧化铝载体的替代材料的潜力。
结果发表在International Journal of Hydrogen Energy:
ZQ Wang, S Nanda, GX Xu, JA. Kozinski, Zhen Fang*, Hydrogen production from biomass via hydrothermal gasification using Ni–Ce catalysts supported on Kaolin, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 193 (2025), 152353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2025.152353