Microbial Lipid Production from Both Rice Straw Hydrolysates and Recycled Pretreated Glycerol
Microbial Lipid Production from Both Rice Straw Hydrolysates and Recycled Pretreated Glycerol
Recently, PhD student Mr. Song Tang supervised by Prof. Zhen FANG produced microbial lipid from both rice straw hydrolysates and recycled pretreated glycerol. First, lipid fermentation of glucose via Cryptococcus curvatus was optimized by response surface methodology. Variables were selected by Plackett–Burman design, and optimized by central composite design, achieving 4.9 g/L total lipid and 0.16 g/g lipid yield, and increased further as glucose increased from 30 to 50 g/L. It was found that lipid content rapidly decreased from 44.5% to 6.4% as lignin (0.5 g/L) was added, which would inhibit lipid accumulation for hydrolysate and recycled glycerol. Secondly, these fermentation conditions were further used for rice straw hydrolysates. After glycerol-FeCl3 pretreatment (0.06 mol/L FeCl3, 150 °C and 20 min), 72% lignin of rice straw was removed with glucose yield increased by 2.4 times to 74.3% at 20% substrate loading and 3 FPU/g dry substrate. Its hydrolysates were separated for lipid fermentation, producing high total lipid (8.8 g/L) and lipid yield (0.17 g/g). Finally, recycled glycerol reached the maximum total lipid of 7.2 g/L and high lipid yield of 0.16 g/g. Based on the calculation, 2.9 g total lipid would be produced from 1 g rice straw and the recycled glycerol, with a similar composition to soybean oil.
The results were published:
S Tang, Q Dong, Zhen Fang*, WJ Cong, H Zhang, Microbial Lipid Production from Both Rice Straw Hydrolysates and Recycled Pretreated Glycerol, Bioresource Technology, 312, 123580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123580.
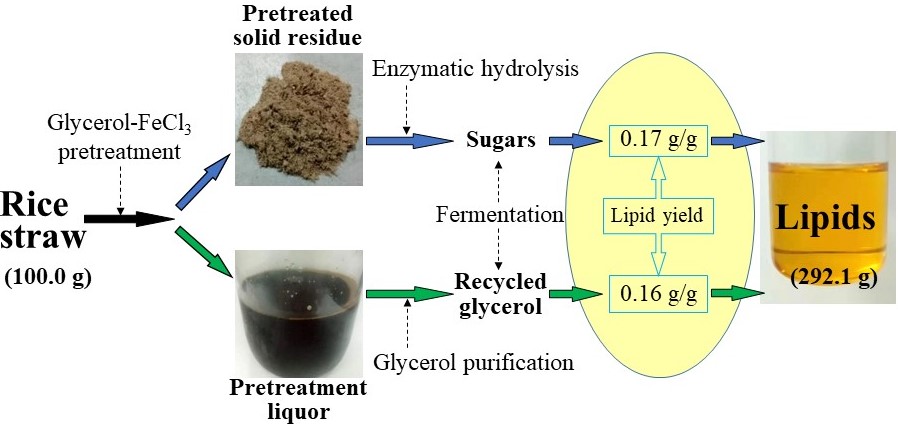
Microbial lipid production from both rice straw hydrolysates and recycled pretreated glycerol(水稻秸秆经甘油-氯化铁预处理后,酶水解,将秸秆水解产物和预处理液中纯化的甘油作为碳源,通过弯曲隐球菌高效生产油脂。)
—————————————————————
稻秆和废弃甘油发酵生产微生物油脂
最近,博士生唐松(男)同学在方老师的指导下,利用稻秆水解液和预处理液中纯化的甘油发酵生产微生物油脂。首先,通过响应面优化弯曲隐球菌发酵葡萄糖产油脂,通过Plackett-Burman实验筛选出显著性因素,设计中心组合实验以优化油脂产量,在最佳发酵条件,总油脂量为4.9 g/L,油脂产率达到0.16 g/g,并通过增加葡萄糖浓度以进一步提高了其产油脂量。但在添加木质素(0.5 g/L)后,酵母胞内油脂含量从44.5%迅速降低至6.4%,这表明木质素会抑制胞内油脂的积累。此后,在优化的发酵条件下,利用稻秆水解产物发酵产微生物油脂。通过甘油-氯化铁预处理(150 °C 和 20 min),稻秆中72%木质素被去除,酶解率较未处理前提高了2.4倍。在3 FPU/g干基和20%基质浓度条件下,酶水解72 h后,预处理后稻秆的酶解率高达74.3%。基于响应面优化的最佳葡萄糖产油脂的发酵条件,在将分离的秸秆水解产物作为碳源,产出油脂8.8 g/L,同时油脂产率也达到了0.17 g/g。最后,利用预处理液中纯化的甘油发酵生产微生物油脂,总油脂量最高达到7.2 g/L,并获得了高水平的油脂产率(0.16 g/g)。通过物料质量平衡分析,1 g稻秆及其预处理中所用甘油将产出2.9 g油脂,其脂肪酸组成也相似于大豆油。
结果发表在Bioresource Technology:
S Tang, Q Dong, Zhen Fang*, WJ Cong, H Zhang, Microbial Lipid Production from Both Rice Straw Hydrolysates and Recycled Pretreated Glycerol, Bioresource Technology, 312, 123580 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123580.