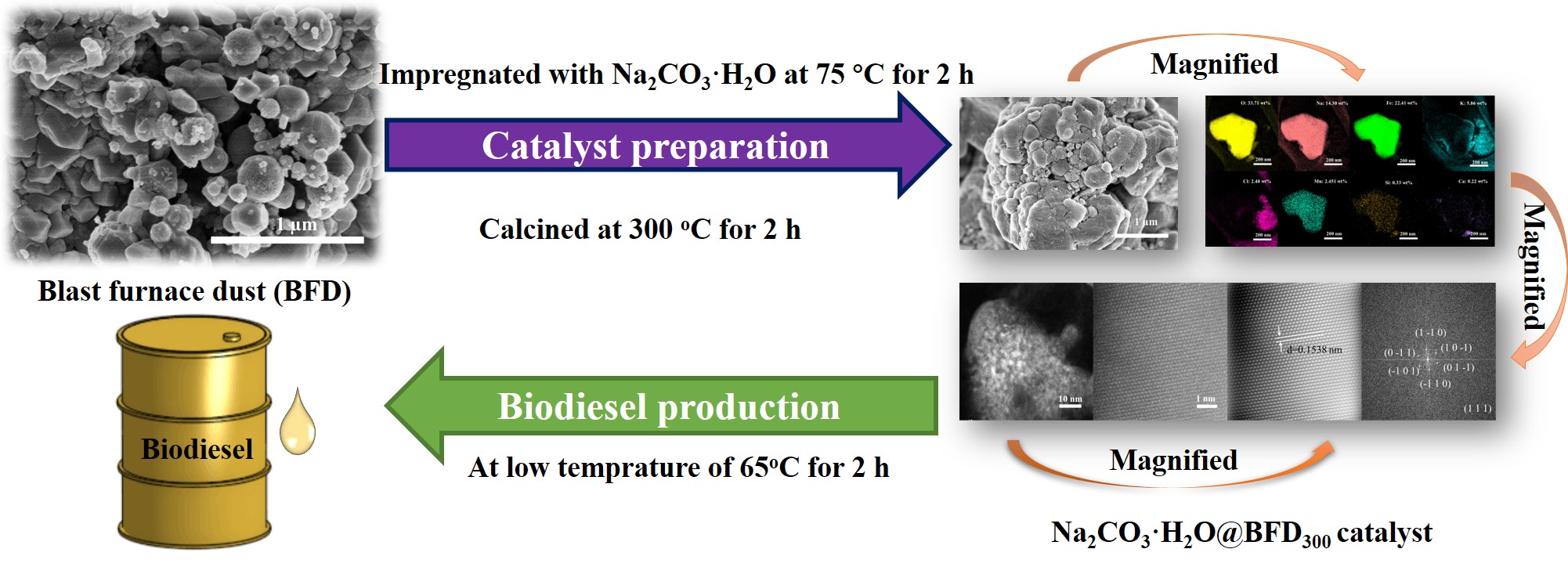
增强二元醇醚化木质素Enhancing α-etherification of lignin in Eucalyptus diol pretreatment to improve lignin monomer production
星期三, 8 6 月, 2022Enhancing α-etherification of lignin in Eucalyptus diol pretreatment to improve lignin monomer production
Recently, Dr. Chengyu Dong and Prof. Zhen Fang, collaborated with Prof. G Cravotto at University of Turin (Italy) and Dr. S-Y Leu at Hong Kong Polytechnic University published a paper about enhancing α-etherification of lignin in Eucalyptus diol pretreatment.
In this work, α-etherification of lignin in diol pretreatment was selectively enhanced at mild temperature for lignin isolation and subsequent valorisation. More than 90% of lignin was removed from Eucalyptus at 120 °C in diol (ethylene glycol and 1,4-butanediol) pretreatment, resulting in >90% cellulose conversion in 24 h at 7.5 FPU/g glucan cellulase loading. Subsequent catalytic transfer hydrogenolysis of the isolated lignins with Ru/C in ethanol gave 15% monomer yield on native lignin basis, 5 times of that from the technical ethanol process (170 °C). HSQC NMR analysis revealed that diol pretreated lignin (120 °C) contained ~23% α-etherified β-O-4 interunit bonds, indicating that lignin degradation (i.e. cleavage of β-O-4 bonds) was suppressed via etherification by grafting a hydroxyl group at the α position of lignin. This finding was consistent with the isolated lignin (120 °C) had less number of phenolic OH and higher molecular weight via 31P NMR and GPC analysis. 31P NMR analysis also revealed that diol isolated lignin contained more numbers of aliphatic OH than ethanol-isolated lignin, which increased lignin solubility and maintained the high yield (>80%) of isolated lignin from Eucalyptus at 120 °C as expected. In summary, diol pretreatment of woody biomass can effectively isolate more lignin for hydrogenolysis to valued-added monomers without compromising the isolated yield of lignin and hydrolysis yield of remained cellulose.
Related results were published in Industry crops and products:
CY Dong, XZ Meng, S-Y Leu, LJ Xu, ZL Wu, G Cravotto, Zhen Fang*, Enhancing a-Etherification of Lignin in Eucalyptus Diol Pretreatment to Improve Lignin Monomer Production, Industrial Crops and Products, 185, 115130, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115130 (2022).
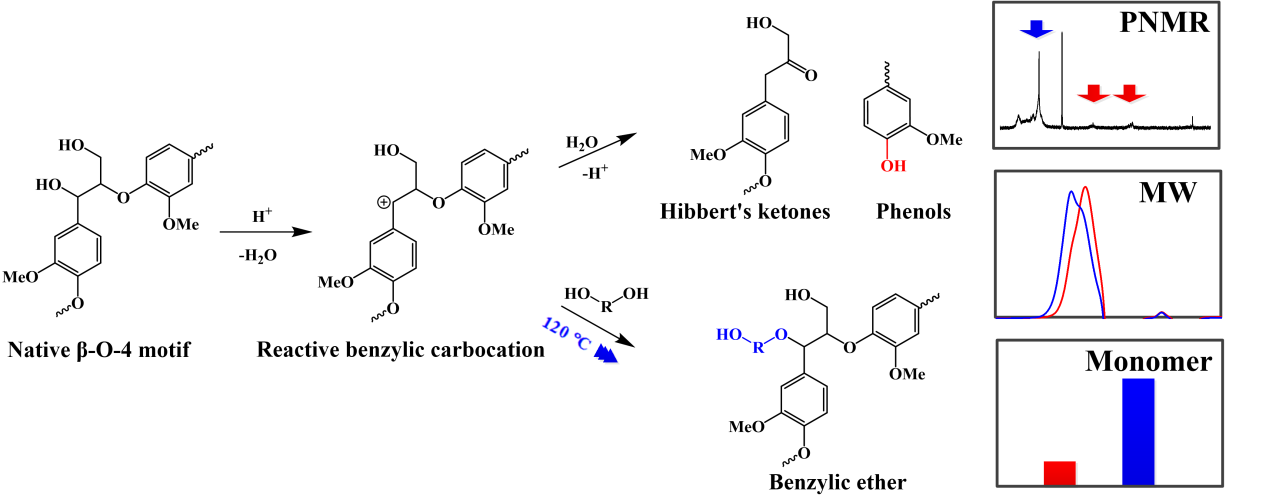
Enhancing α-etherification of lignin by diol pretreatment at mild temperature (120 °C) to isolate lignin for producing 5 times monomer yield of that from technical ethanol pretreatment (170 °C) by hydrogenolysis. (在二元醇预处理过程中,木质素的α-醚化在温和温度(120 ℃)下增强,其分离木质素氢解单体收率达到工业乙醇预处理(170 ℃)单体收率的5倍)
董澄宇博士在国际学术期刊Industry crops and products发表学术论文
最近,农业工程期刊Industry crops and products (第一署名单位为南京农业大学,第一作者为董澄宇博士,通讯作者为方真教授, 合作单位意大利都灵大学G Cravotto教授和香港理工大学S-Y Leu 博士)发表了一篇关于提高桉树二醇预处理过程中木质素α-醚化的文章。
在该研究中,二元醇预处理中木质素a-醚化在温和的温度下被选择性地增强,可高效分离木质素并利于木质素的高值化利用。在120 ℃,二元醇(乙二醇和1,4-预处理的桉树木质素去除率达到90%以上,纤维素在24小时内转化率即为90%。随后在乙醇中用钌/碳催化氢解木质素,单体产率为15%,是工业乙醇预处理(170 ℃)的5倍。二维核磁共振分析表明,二元醇预处理木质素(120 °C) 包含23%α-醚化β-O-4化学键,表明木质素降解(即β-O-4键的断裂)被在木质素α-醚化抑制。这个结果与木质素的核磁磷谱分析和凝胶色谱结果分析抑制,该条件下分离的木质素酚羟基含量少,分子量高。核磁磷谱分析还表明,二元醇分离的木质素比乙醇分离的木质素含有更多的脂肪族羟基,这增加了木质素的溶解度并保持了较高的分离效率(120 ℃时,桉树木质素的分离率为80%)。综上所述,木质生物质的二醇预处理可以有效地分离出更多的木质素氢解为高附加值的单体,而不影响木质素的分离效率和纤维素的水解效率。
结果发表在Industry crops and products:
CY Dong, XZ Meng, S-Y Leu, LJ Xu, ZL Wu, G Cravotto, Zhen Fang*, Enhancing a-Etherification of Lignin in Eucalyptus Diol Pretreatment to Improve Lignin Monomer Production, Industrial Crops and Products, 185, 115130, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115130 (2022).
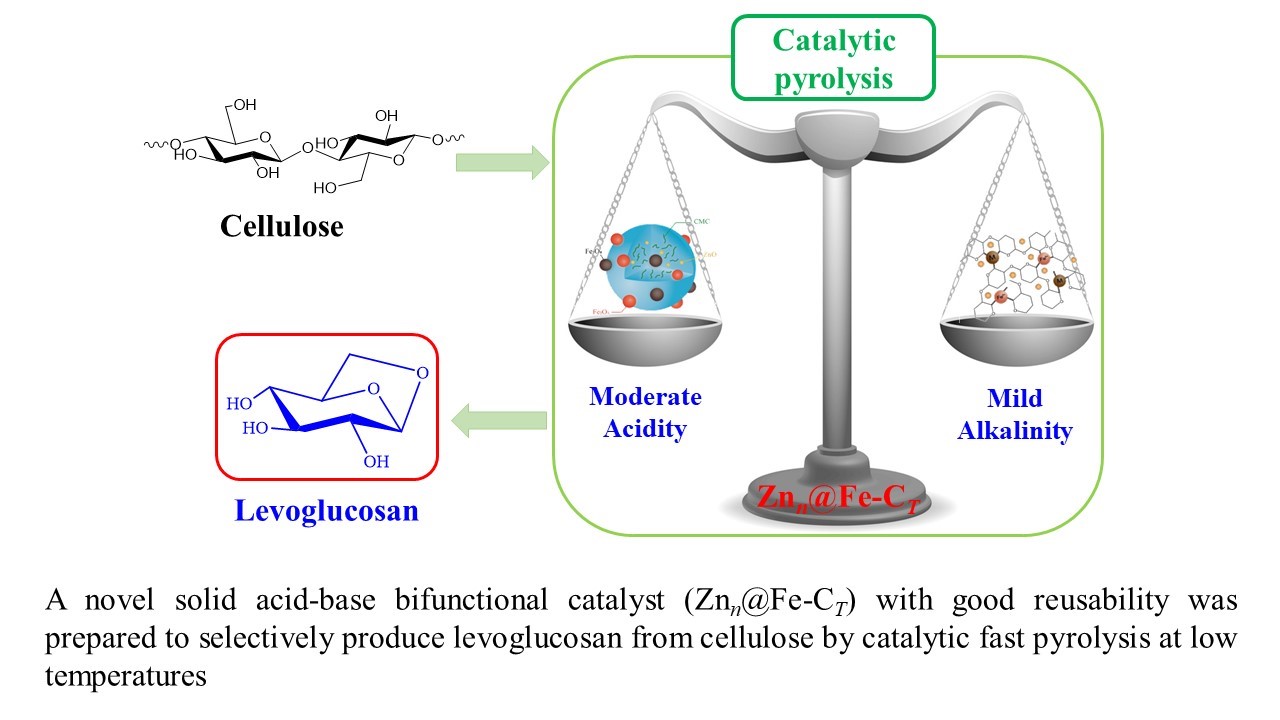 Production of Levoglucosan via Catalytic Pyrolysis of Cellulose at Low Temperature with Znn@Fe-CT acid-base bifunctional magnetic catalyst磁性固体酸碱两性催化剂Znn@Fe-CT催化纤维素定向热解制备左旋葡聚糖
Production of Levoglucosan via Catalytic Pyrolysis of Cellulose at Low Temperature with Znn@Fe-CT acid-base bifunctional magnetic catalyst磁性固体酸碱两性催化剂Znn@Fe-CT催化纤维素定向热解制备左旋葡聚糖