UK-Jiangsu Sustainable Future of Plastics (UKJS)
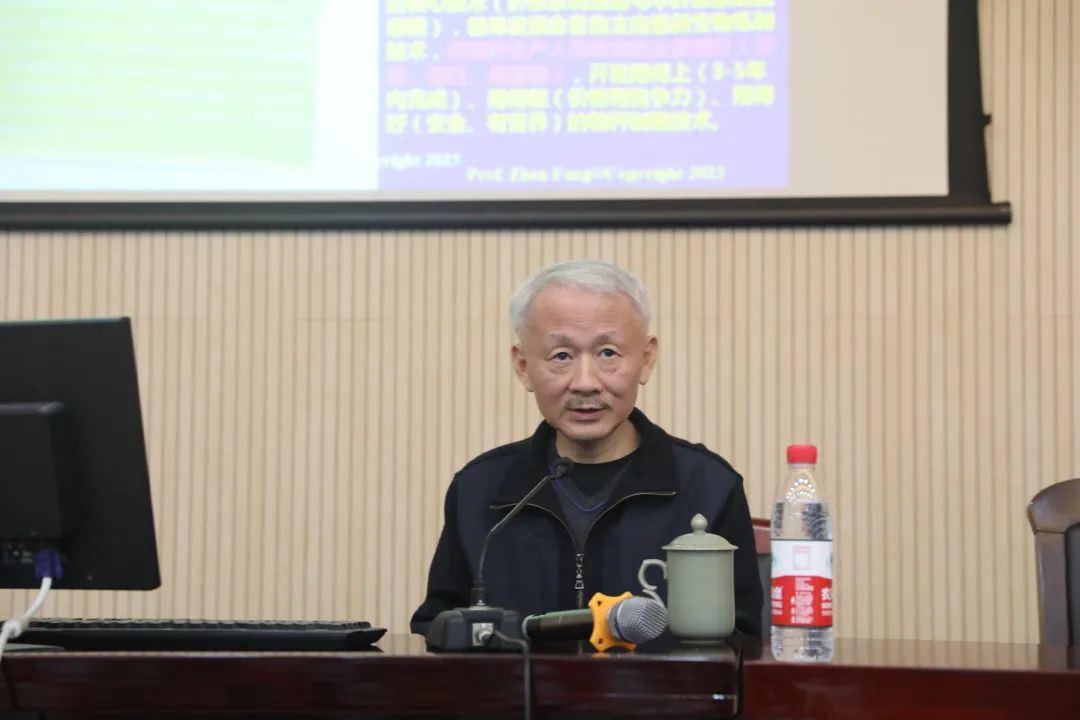
The UK-Jiangsu Sustainable Future of Plastics (UKJS, Virtual Conference) was successfully held on November 16, 2023 and hosted by University of Liverpool and Nanjing Agricultural University. Six Scholars from UK and Jiangsu shared their most recent research activities on catalytic conversion, pyrolytic-catalysis, biodegradation and upcycling, porous carbon synthesis, and PET valorization. The purpose is to promote international academic exchange and cooperation on sustainable management and development of plastics.
Organization Committee
Chairs:
Professor Xin Tu, University of Liverpool, UK
Professor Zhen Fang (Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering, FCAE), Nanjing Agricultural University, China
Secretary: Dr. Wei Chen (Email: weichen@njau.edu.cn)
URL:https://biomass-group.njau.edu.cn/info/1016/1952.htm
https://woodrefinery.com/zhenfang/%e6%b1%9f%e8%8b%8f-%e8%8b%b1%e5%9b%bd%e5%a1%91%e6%96%99%e4%bc%9a%e8%ae%aeuk-jiangsu-sustainable-future-of-plastics-ukjs/
Videos:
Bilibili: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wb4y1T7Xp/?vd_source=a9e383d02bf07f9a4fcdf535ed50b757
YouTube: https://youtu.be/bsAGPzKDdMY?si=c60wS2zR14eHfGZ9
Lectures
- 1.The Development and Future of Plastic (Agricultural Film) in Chinese Agriculture
Professor Haitao Zhao, Yangzhou University
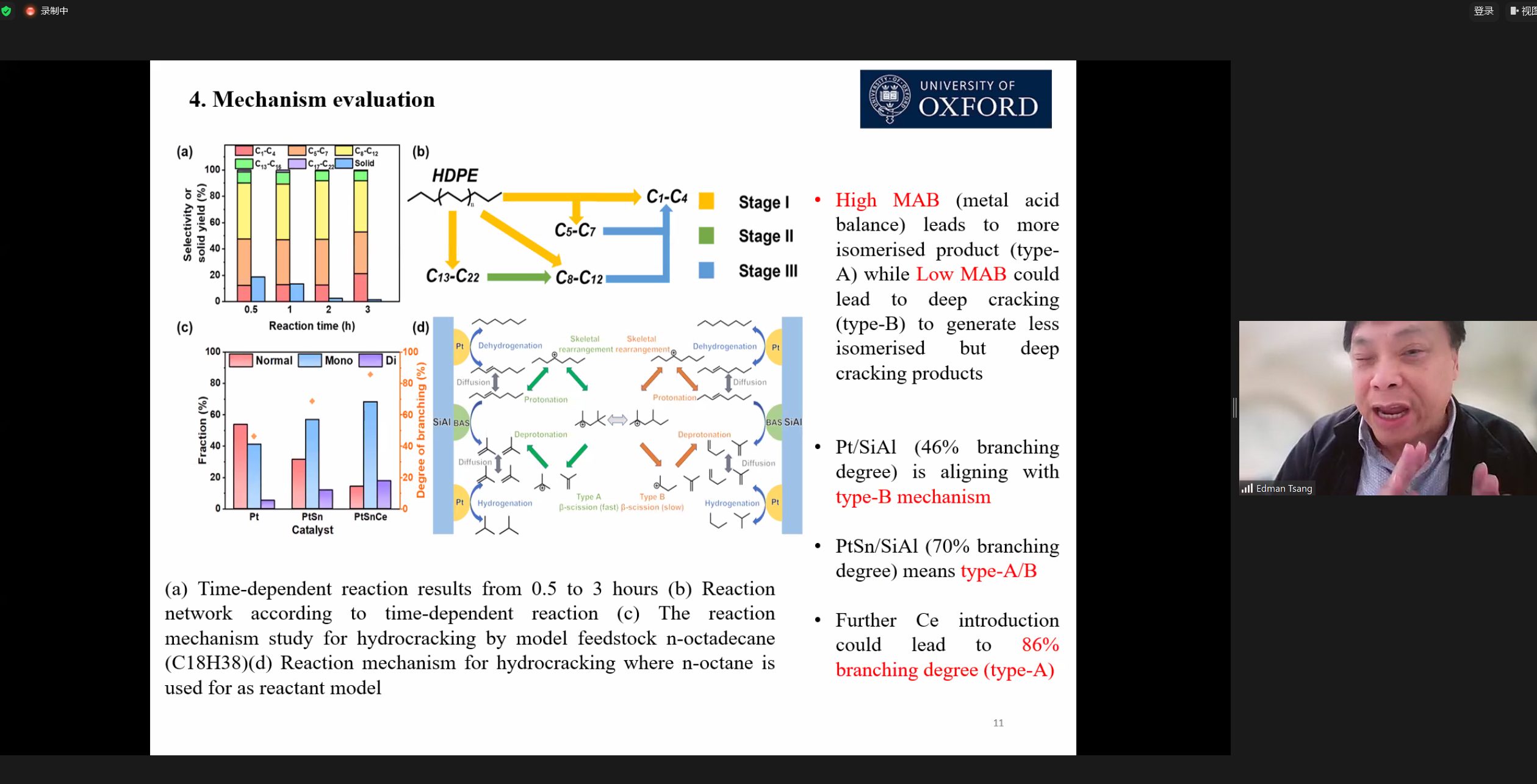
- 2.The Challenges and Opportunities in Catalytic Conversion of Thermoplastics for Chemicals
Edman Tsang, University of Oxford
- 3.Two-stage Pyrolysis-catalysis of Waste Plastics
Paul Williams, University of Leeds
- 4.Biodegradation and UPcycling of Waste Plastics by MIX-UP
Min Jiang, Nanjing Tech University
- 5.Sustainable Plastic Management: Synthesizing Porous Carbons for CO2 Capture towards a Circular Economy
Xiangzhou Yuan, Southeast University
- 6.Valorization of PET into Aromatic Nitriles via Catalytic Pyrolysis with Active Ammonia Source
Lujiang Xu, Nanjing Agricultural University
Conference Photos

Professor Edman Tsang, University of Oxford
Prof. Paul Williams, University of Leeds
Bio

Dr. Xin Tu is a Professor (Chair in Plasma Catalysis) at the University of Liverpool. His research focuses on plasma chemistry and plasma catalysis for environmental clean-up and sustainable production of fuels and chemicals. He has published 7 book chapters and over 200 peer-reviewed journal papers (H-index 63, >11500 citations) in leading international journals. He is the inventor of 5 international patents associated with plasma production of fuels and chemicals. He has given over 90 invited talks at major international conferences and chaired/co-chaired 7 international conferences. He led a group of 16 leading scientists to deliver the 2020 Plasma Catalysis Roadmap (J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2020, 53, 443001, 51 pages, downloaded >28000). He is the Topic Editor of a New Flagship Programme – Advances in Plasmas for a Sustainable Future launched by J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. (IOP).

Prof. Zhen Fang
He obtained his BSc, MSc and PhD degrees from China Agricultural University (Agricultural Engineering, Beijing) and PhD degree from McGill University (Materials Engineering, Montreal) as well as received further postdoc training in Chemical Engineering in Spain (Marie Curie Fellowship, Universidad de Zaragoza). He is the inventor of the “fast hydrolysis” process. He is Editor-in-Chief of Springer Book Series – Biofuels and Biorefineries, Elected Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering (2021), Associate Editor of Biotechnol Biofuels (Springer), and Associate Editor of J Supercrit Fluid (Elsevier, 2018-21). He is also one of the editorial (advisory) board members of Biofuel Bioprod Bior (Wiley, 2012-18), Energy Sustain Soc (Springer), Energy Policy Res (Taylor & Francis, 2016-2018), Polymers (MDPI, Basel, Switzerland), and Comb Chem High T Scr. Prof. Fang is specializing in thermal/biochemical conversion of biomass, nanocatalysts synthesis and their applications, as well as pretreatment of biomass for biorefineries and supercritical fluid processes. He is listed in the “Most Cited Chinese Researchers” every year from 2014 to 2022.

Dr. Edman Tsang is a Professor of Inorganic Chemistry and Head of Wolfson Catalysis Laboratory at Oxford Chemistry since 2007. He also serves as the catalysis theme co-ordinator in the department. His main research interests are on nanomaterials and heterogeneous catalysis concerning energy and environment which include developments of catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic technologies for green chemistry, fine chemicals, cleaner combustion, energy storages, processes and production, ammonia and hydrogen technologies including fuel cells, etc. Particular expertise is in design and architecture of nanocatalysts and their in situ diffraction and spectroscopic characterization, which can lead to understanding of catalytic surfaces and interfaces. From 2004-2006, he was the personal chair professor of the Chemistry department at Reading University, serving as Director of Research, followed by the appointment of the Head of Reading Surface and Catalysis Research Centre (2000-2004). He was a Royal Society University Research Fellow between Oxford and Reading (1995-2000). He has more than 400 referred publications with h-index of about 70, 6 book chapters and 16 patents. He has been the top 10% highly cited researcher in RSC general chemistry (2014-2016). He has won a number of international awards including WGO award, London University (1993); IChemE award on iAc innovation in catalysis (2005), IChemE NES Awards for Novel Engineering-shortlisted candidate (2008); Royal Society Kan Tong Po Professorship (2012); Royal Society Green Chemistry award (2012) and Royal Society Surfaces and Interfaces award (2013), etc. He has recently found OXGRIN www.oxgrin.com for the development and commercialisation of breakthrough catalytic technologies in green energy applications.

Dr. Paul Williams is Professor of Environmental Engineering at The University of Leeds and has a research background in both applied chemistry and process engineering. He is a Chartered Engineer and Fellow of the Institute of Energy. He has published more than 500 academic papers in the area of environmental engineering, including waste and biomass pyrolysis, gasification and waste incineration. He has also authored a second edition of a text book entitled ‘Waste Treatment and Disposal’ (John Wiley & Sons, 2005). He has an ‘h’ index of 85 and more than 25,000 citations to his work (Google Scholar). In addition, he has been awarded 28 EPSRC research grants and numerous industrial research grants, totalling over £15M. His research work has been honoured by several awards including the Steetley-Magnesia Award, the Redlands Minerals Award, the Lubbock-Sambrook Award and the Distinguished Guest Lecturer Medal by the Environmental Chemistry Group of the Royal Society of Chemistry. He is a member of the Editorial Boards of the journals, Environmental Technology, Waste & Biomass Valorization, Biofuels, Fuel and editor of Journal of the Energy Institute

Dr. Xiangzhou Yuan is a Full Professor at the School of Energy and Environment in Southeast University, Nanjing, China. His academic background covers thermochemical valorization of biomass and organic waste, greenhouse gas adsorption and separation, syntheses, characterizations, and applications of porous carbons. He has published over 70 refereed journal articles including Nat. Rev. Earth Environ., Matter, Prog. Mater. Sci. Dr. Yuan registered 8 Korean patents and achieved 2 technology transfer (KR10-2197821 & KR10-1650191). He is also active in serving as the R&D Director of Sun Brand Industrial Inc. from 2020, and an Academic Committee Member of the International Cooperation Research Centre of Carbon Capture in Ultra-low Energy-consumption, Tianjin, China from 2018. Moreover, he has been invited to deliver keynote and invited speeches for over 20 international conferences in energy, engineering, and environmental fields. He also serves as Guest Editors (Chemical Engineering Journal, Applied Energy, Advances in Applied Energy, etc.), and Youth Editorial Board Members (Biochar, Carbon Research, Resources Chemicals and Materials, etc.).

Dr. Lujang Xu, Associate Professor at Nanjing Agricultural University, with research focuses on thermal chemical conversion of biomass and solid organic waste towards the production of high-value chemicals (pharmaceuticals, pharmaceutical intermediates) and high-quality liquid fuels. He has led more than 10 projects from National Natural Science Foundation of China (2), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (2), etc. He has published over 20 papers (first or corresponding author,) in leading energy and environmental journals such as Green Chemistry, Bioresource Technology, Energy and Waste Management, and has been awarded over 10 national invention patents.

Prof. Min Jiang, Second-degree Professor, Ph.D. Supervisor, and a National Major Talent Project Inductee, currently serves as the dean of the Science Research Institute of Nanjing Tech University, the executive dean of the Jiangsu Academy of Chemical Inherent Safety, the director of Sino-German Laboratory for Bio-refinery of Waste Carbon Resources, Director of Nanjing Synthetic Biological Industry Innovation Center, Director of China Biotech Fermentation Industry Association, Executive Director and Deputy Secretary-General of the Jiangsu Province Biotechnology Association, China and Germany (Jiangsu – Baden-Württemberg) bilateral cooperative Chinese coordinator, Visiting Professor of Karlsruher Institut für Technologie(KIT)in Germany. Dr. Min Jiang devotes long-term effort to research in advanced biological manufacturing. In the past five years, he published over 130 academic papers as the first/(common) corresponding author in the authoritative academic journals such as Trends Biotechnol, ACS Synth Biol, Biotechnol Biong with more than 2000 other citations.

Dr. Haitao Zhao, professor, doctoral director, deputy director of Science and Technology Department of Yangzhou University. He is the person in charge of national first-class courses, an expert of Jiangsu Modern Agriculture (Watermelon) Industrial Technology System Soil Improvement Innovation Team, and the first batch of Jiangsu Cultivated Land Soil Pollution Prevention and Control Experts. He is mainly engaged in organic solid waste resource treatment, soil fertilizer and agricultural environmental protection, water environment and water resources and other fields of research work. He has presided over more than 20 projects, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Public Welfare Industry Research Special Project, and the Agricultural Science and Technology Support Program of Jiangsu Province. He has published more than 100 research papers, obtained 6 authorized invention patents, and edited 2 monographs.
江苏-英国塑料的可持续未来研讨会(UKJS)成功举办
实现绿色可持续的循环经济转型是应对由于塑料广泛使用带来的包括污染、废物及微塑料大量产生等问题的重要手段。2023年11月16日,英国-江苏塑料的可持续未来研讨会(UKJS)在线上隆重召开,探讨有关废塑料可持续管理和解决策略的挑战和最新发展动态。
本次研讨会(UKJS)由利物浦大学和南京农业大学联合举办,利物浦大学屠昕教授和南京农业大学方真教授为大会主席,来自英国和江苏的专家汇聚一堂分享废塑料应用管理方面的最新进展。扬州大学赵海涛教授、牛津大学Edman Tsang教授、利兹大学Paul Williams教授、南京工业大学姜岷教授、东南大学袁湘洲教授和南京农业大学徐禄江副教授分享包括催化转化、热解催化、生物降解和升级再循环、多孔碳合成和PET高值转化在内的一系列创新技术。会议旨在增进各学者在塑料可持续管理和发展研究方面的国际学术交流和合作。
URL:https://biomass-group.njau.edu.cn/info/1016/1952.htm
https://woodrefinery.com/zhenfang/%e6%b1%9f%e8%8b%8f-%e8%8b%b1%e5%9b%bd%e5%a1%91%e6%96%99%e4%bc%9a%e8%ae%aeuk-jiangsu-sustainable-future-of-plastics-ukjs/
演讲录像:
B站:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wb4y1T7Xp/?vd_source=a9e383d02bf07f9a4fcdf535ed50b757
YouTube: https://youtu.be/bsAGPzKDdMY?si=c60wS2zR14eHfGZ9
























