冶金渣处理废水A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism
星期五, 4 11 月, 2022A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism
Recently, Dr Yi-Tong Wang (Associate Prof., College of Metallurgy and Energy, North China University of Science and Technology) and Prof. Zhen Fang published a review article in Journal of Cleaner Production about using metallurgical slag to treatment wastewater.
Metallurgical slag as a by-product of the metallurgical industry not only has huge storage capacity and low price, but also causes serious damage to the environment and threatens the safety of human life by heavy metal in metallurgical slag leaching. The approach of metallurgical slag used to remove pollutants in wastewater is considered to achieve the purpose of “using waste to treat waste”. This review focuses on three pretreatment methods of metallurgical slag including acid/alkali pretreatment, mixed pretreatment, and core-shell structure pretreatment, and their structural properties and performance optimization after pretreatment. The removal mechanism of typical pollutants, catalytic performance, reaction conditions, and recyclability of metallurgical slag such as steel slag, blast furnace slag, red mud, copper slag, and manganese slag are summarized and compared.
Related results were accepted in Journal of Cleaner Production:
Rui Ji, Tian-Ji Liu, Le-Le Kang, Yi-Tong Wang, Jun-Guo Li, Fu-Ping Wang, Qing Yu, Xiao-Man Wang, Huan Liu, Hua-Wei Guo, Wen-Long Xu, Ya-Nan Zeng, Zhen Fang. A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism. Accepted. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022.
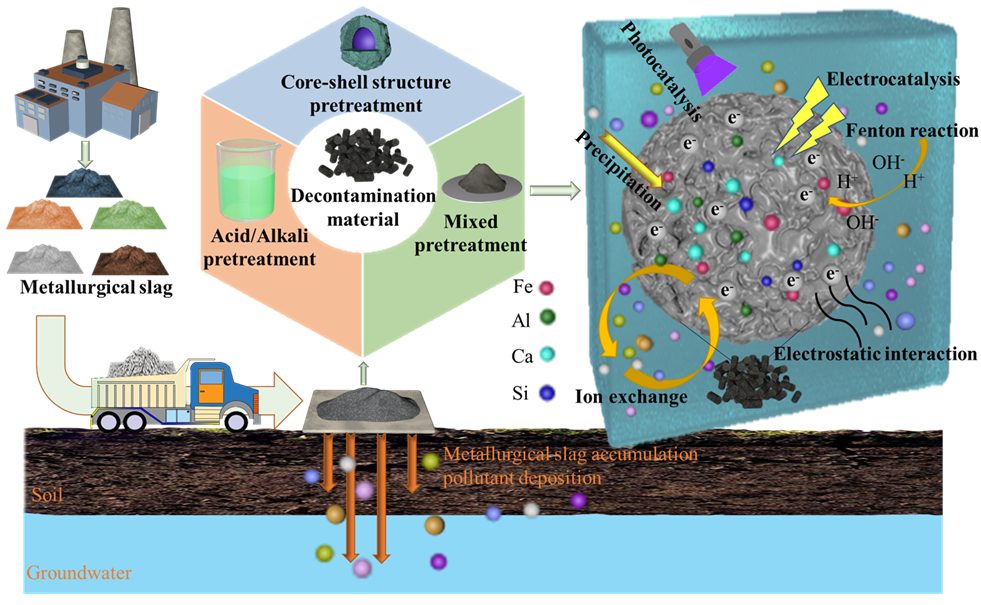
After pretreatment, metallurgical slag can effectively remove heavy metals, dyes, antibiotics and other pollutants from wastewater. 冶金渣经过预处理后可高效去除废水中的重金属、染料和抗生素等污染物。
冶金渣高效处理废水的研究进展:预处理、性能和机理
最近,王一同博士(华北理工大学冶金与能源学院副教授)和方真教授在国际学术期刊Journal of Cleaner Production 发表题为“冶金渣高效处理废水的研究进展:预处理、性能和机理”的综述性论文。
冶金渣是冶金工业的副产品,不仅储量巨大而且价格低廉。但是冶金渣堆积浸出过程中的重金属对环境造成严重破坏,威胁人类生命安全。使用冶金渣去除废水中污染物可以达到“以废治废”的目的。综述了冶金渣的三种预处理方法,包括酸碱预处理、混合预处理和核壳结构预处理,以及预处理后的结构性能和性能优化。对钢渣、高炉渣、赤泥、铜渣和锰渣等冶金渣的典型污染物去除机理、催化性能、反应条件和可回收性进行了总结和比较。该论文为冶金渣应用于废水处理方面提供了新思路。详情可见:
Rui Ji, Tian-Ji Liu, Le-Le Kang, Yi-Tong Wang, Jun-Guo Li, Fu-Ping Wang, Qing Yu, Xiao-Man Wang, Huan Liu, Hua-Wei Guo, Wen-Long Xu, Ya-Nan Zeng, Zhen Fang. A review of metallurgical slag for efficient wastewater treatment: Pretreatment, performance and mechanism. Accepted. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022.